“关于:Java网络IO编程(BIO、NIO、AIO)”的版本间差异
跳到导航
跳到搜索
小 (Eijux移动页面关于:Java应用BIO、NIO、AIO至关于:Java网络IO编程(BIO、NIO、AIO),不留重定向) |
|||
| 第22行: | 第22行: | ||
== BIO(blocking IO) == | == BIO(blocking IO) == | ||
=== 传统的BIO编程 === | |||
网络编程的基本模型是'''C/S'''模型,即'''两个进程间的通信''': | |||
: 服务端提供IP和监听端口,客户端通过连接操作想服务端监听的地址发起连接请求,通过三次握手连接,如果连接成功建立,双方就可以通过套接字进行通信。 | |||
: '''ServerSocket'''负责绑定IP地址,启动监听端口;'''Socket'''负责发起连接操作。连接成功后,双方通过输入和输出流进行同步阻塞式通信。 | |||
简单的描述一下BIO的服务端通信模型: | |||
: 采用BIO通信模型的服务端,通常由一个独立的Acceptor线程负责监听客户端的连接,它接收到客户端连接请求之后为每个客户端创建一个新的线程进行链路处理没处理完成后,通过输出流返回应答给客户端,线程销毁。即典型的一请求一应答通宵模型。 | |||
特点: | |||
* 缺乏弹性伸缩能力,服务端的线程个数和客户端并发访问数呈 '''1:1''' 的正比关系。 | |||
示例: | |||
* Server: | |||
*: <syntaxhighlight lang="java" highlight=""> | |||
package com.anxpp.io.calculator.bio; | |||
import java.io.IOException; | |||
import java.net.ServerSocket; | |||
import java.net.Socket; | |||
/** | |||
* BIO服务端源码 | |||
* @author yangtao__anxpp.com | |||
* @version 1.0 | |||
*/ | |||
public final class ServerNormal { | |||
// 默认的端口号 | |||
private static int DEFAULT_PORT = 12345; | |||
// 单例的ServerSocket | |||
private static ServerSocket server; | |||
//根据传入参数设置监听端口,如果没有参数调用以下方法并使用默认值 | |||
public static void start() throws IOException{ | |||
//使用默认值 | |||
start(DEFAULT_PORT); | |||
} | |||
// 这个方法不会被大量并发访问,不太需要考虑效率,直接进行方法同步就行了 | |||
public synchronized static void start(int port) throws IOException{ | |||
if(server != null) return; | |||
try{ | |||
// 通过构造函数创建ServerSocket | |||
// 如果端口合法且空闲,服务端就监听成功 | |||
server = new ServerSocket(port); | |||
System.out.println("服务器已启动,端口号:" + port); | |||
//通过无线循环监听客户端连接 | |||
//如果没有客户端接入,将阻塞在accept操作上。 | |||
while(true){ | |||
Socket socket = server.accept(); | |||
//当有新的客户端接入时,会执行下面的代码 | |||
//然后创建一个新的线程处理这条Socket链路 | |||
new Thread(new ServerHandler(socket)).start(); | |||
} | |||
}finally{ | |||
//一些必要的清理工作 | |||
if(server != null){ | |||
System.out.println("服务器已关闭。"); | |||
server.close(); | |||
server = null; | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
*: <syntaxhighlight lang="java" highlight=""> | |||
package com.anxpp.io.calculator.bio; | |||
import java.io.BufferedReader; | |||
import java.io.IOException; | |||
import java.io.InputStreamReader; | |||
import java.io.PrintWriter; | |||
import java.net.Socket; | |||
import com.anxpp.io.utils.Calculator; | |||
/** | |||
* 客户端线程 | |||
* @author yangtao__anxpp.com | |||
* 用于处理一个客户端的Socket链路 | |||
*/ | |||
public class ServerHandler implements Runnable{ | |||
private Socket socket; | |||
public ServerHandler(Socket socket) { | |||
this.socket = socket; | |||
} | |||
@Override | |||
public void run() { | |||
BufferedReader in = null; | |||
PrintWriter out = null; | |||
try{ | |||
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); | |||
out = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(),true); | |||
String expression; | |||
String result; | |||
while(true){ | |||
//通过BufferedReader读取一行 | |||
//如果已经读到输入流尾部,返回null,退出循环 | |||
//如果得到非空值,就尝试计算结果并返回 | |||
if((expression = in.readLine())==null) break; | |||
System.out.println("服务器收到消息:" + expression); | |||
try{ | |||
result = Calculator.cal(expression).toString(); | |||
}catch(Exception e){ | |||
result = "计算错误:" + e.getMessage(); | |||
} | |||
out.println(result); | |||
} | |||
}catch(Exception e){ | |||
e.printStackTrace(); | |||
}finally{ | |||
//一些必要的清理工作 | |||
if(in != null){ | |||
try { | |||
in.close(); | |||
} catch (IOException e) { | |||
e.printStackTrace(); | |||
} | |||
in = null; | |||
} | |||
if(out != null){ | |||
out.close(); | |||
out = null; | |||
} | |||
if(socket != null){ | |||
try { | |||
socket.close(); | |||
} catch (IOException e) { | |||
e.printStackTrace(); | |||
} | |||
socket = null; | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
* Client: | |||
*: <syntaxhighlight lang="java" highlight=""> | |||
package com.anxpp.io.calculator.bio; | |||
import java.io.BufferedReader; | |||
import java.io.IOException; | |||
import java.io.InputStreamReader; | |||
import java.io.PrintWriter; | |||
import java.net.Socket; | |||
/** | |||
* 阻塞式I/O创建的客户端 | |||
* @author yangtao__anxpp.com | |||
* @version 1.0 | |||
*/ | |||
public class Client { | |||
// 默认的端口号 | |||
private static int DEFAULT_SERVER_PORT = 12345; | |||
private static String DEFAULT_SERVER_IP = "127.0.0.1"; | |||
public static void send(String expression){ | |||
send(DEFAULT_SERVER_PORT,expression); | |||
} | |||
public static void send(int port,String expression){ | |||
System.out.println("算术表达式为:" + expression); | |||
Socket socket = null; | |||
BufferedReader in = null; | |||
PrintWriter out = null; | |||
try{ | |||
socket = new Socket(DEFAULT_SERVER_IP,port); | |||
in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); | |||
out = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(),true); | |||
out.println(expression); | |||
System.out.println("___结果为:" + in.readLine()); | |||
}catch(Exception e){ | |||
e.printStackTrace(); | |||
}finally{ | |||
// 必要的清理工作 | |||
if(in != null){ | |||
try { | |||
in.close(); | |||
} catch (IOException e) { | |||
e.printStackTrace(); | |||
} | |||
in = null; | |||
} | |||
if(out != null){ | |||
out.close(); | |||
out = null; | |||
} | |||
if(socket != null){ | |||
try { | |||
socket.close(); | |||
} catch (IOException e) { | |||
e.printStackTrace(); | |||
} | |||
socket = null; | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
* 测试代码: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java" highlight=""> | *: <syntaxhighlight lang="java" highlight=""> | ||
package com.anxpp.io.calculator.bio; | |||
import java.io.IOException; | |||
import java.util.Random; | |||
/** | |||
* 测试方法 | |||
* @author yangtao__anxpp.com | |||
* @version 1.0 | |||
*/ | |||
public class Test { | |||
// 测试主方法 | |||
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { | |||
// 运行服务器 | |||
new Thread(new Runnable() { | |||
@Override | |||
public void run() { | |||
try { | |||
ServerBetter.start(); | |||
} catch (IOException e) { | |||
e.printStackTrace(); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
}).start(); | |||
// 避免客户端先于服务器启动前执行代码 | |||
Thread.sleep(100); | |||
// 运行客户端 | |||
char operators[] = {'+','-','*','/'}; | |||
Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis()); | |||
new Thread(new Runnable() { | |||
@SuppressWarnings("static-access") | |||
@Override | |||
public void run() { | |||
while(true){ | |||
//随机产生算术表达式 | |||
String expression = random.nextInt(10)+""+operators[random.nextInt(4)]+(random.nextInt(10)+1); | |||
Client.send(expression); | |||
try { | |||
Thread.currentThread().sleep(random.nextInt(1000)); | |||
} catch (InterruptedException e) { | |||
e.printStackTrace(); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
}).start(); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
* 运行结果: | |||
*: <syntaxhighlight lang="java" highlight=""> | |||
服务器已启动,端口号:12345 | |||
算术表达式为:4-2 | |||
服务器收到消息:4-2 | |||
___结果为:2 | |||
算术表达式为:5-10 | |||
服务器收到消息:5-10 | |||
___结果为:-5 | |||
算术表达式为:0-9 | |||
服务器收到消息:0-9 | |||
___结果为:-9 | |||
算术表达式为:0+6 | |||
服务器收到消息:0+6 | |||
___结果为:6 | |||
算术表达式为:1/6 | |||
服务器收到消息:1/6 | |||
___结果为:0.16666666666666666 | |||
... | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
=== 伪异步I/O编程 === | |||
为了改进以上一连接一线程的模型,我们可以使用'''线程池'''来管理这些线程,实现 1 个或多个线程处理 N 个客户端的模型(但是'''底层还是使用的同步阻塞I/O'''),通常被称为“伪异步I/O模型“。 | |||
* 只需要Server端新建线程交给线程池管理即可:【替换上节的“ServerNormal”】 | |||
*: <syntaxhighlight lang="java" highlight="18,41"> | |||
package com.anxpp.io.calculator.bio; | |||
import java.io.IOException; | |||
import java.net.ServerSocket; | |||
import java.net.Socket; | |||
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; | |||
import java.util.concurrent.Executors; | |||
/** | |||
* BIO服务端源码__伪异步I/O | |||
* @author yangtao__anxpp.com | |||
* @version 1.0 | |||
*/ | |||
public final class ServerBetter { | |||
// 默认的端口号 | |||
private static int DEFAULT_PORT = 12345; | |||
// 单例的ServerSocket | |||
private static ServerSocket server; | |||
// 线程池【懒汉式的单例】 | |||
private static ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(60); | |||
// 根据传入参数设置监听端口,如果没有参数调用以下方法并使用默认值 | |||
public static void start() throws IOException{ | |||
//使用默认值 | |||
start(DEFAULT_PORT); | |||
} | |||
//这个方法不会被大量并发访问,不太需要考虑效率,直接进行方法同步就行了 | |||
public synchronized static void start(int port) throws IOException{ | |||
if(server != null) return; | |||
try{ | |||
// 通过构造函数创建ServerSocket | |||
// 如果端口合法且空闲,服务端就监听成功 | |||
server = new ServerSocket(port); | |||
System.out.println("服务器已启动,端口号:" + port); | |||
// 通过无线循环监听客户端连接 | |||
// 如果没有客户端接入,将阻塞在accept操作上。 | |||
while(true){ | |||
Socket socket = server.accept(); | |||
//当有新的客户端接入时,会执行下面的代码 | |||
//然后创建一个新的线程处理这条Socket链路 | |||
executorService.execute(new ServerHandler(socket)); | |||
} | |||
}finally{ | |||
//一些必要的清理工作 | |||
if(server != null){ | |||
System.out.println("服务器已关闭。"); | |||
server.close(); | |||
server = null; | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
如果使用'''CachedThreadPool'''线程池(不限制线程数量),其实除了能自动帮我们管理线程(复用),看起来也就像是 '''1:1''' 的 客户端:线程数 模型, | |||
而使用'''FixedThreadPool'''就有效的控制了线程的最大数量,保证了系统有限的资源的控制,实现了 '''N:M''' 的伪异步I/O模型。 | |||
=== JavaNIO的BIO编程 === | |||
== NIO(non-blocking IO) == | == NIO(non-blocking IO) == | ||
2021年5月13日 (四) 23:46的版本
关于
本文主要讨论 Java 实现 network IO 的三种实现:BIO、NIO、AIO。
什么是 BIO、NIO、AIO?
- 见:“关于:5种I/O模型”
- BIO:“blocking IO”,阻塞IO;
- NIO:“non-blocking IO”,非阻塞IO;
- AIO:“asynchronous IO”,异步IO;
Java 的 NIO API
- 见:“关于NIO”(概念、组件、用法)
需要注意的是:
- Java NIO 是“Java New IO API”,而非“Non-Blocking IO”。二者不是一个概念。
- Java NIO 支持面向缓冲区的、基于通道的IO操作,以更加高效的方式进行文件的读写操作。
- 其 NIO API 既可以实现“Non-Blocking IO”(NIO)和“Asynchronous IO”(AIO),也可以实现“Blocking IO”(BIO)。
BIO(blocking IO)
传统的BIO编程
网络编程的基本模型是C/S模型,即两个进程间的通信:
- 服务端提供IP和监听端口,客户端通过连接操作想服务端监听的地址发起连接请求,通过三次握手连接,如果连接成功建立,双方就可以通过套接字进行通信。
- ServerSocket负责绑定IP地址,启动监听端口;Socket负责发起连接操作。连接成功后,双方通过输入和输出流进行同步阻塞式通信。
简单的描述一下BIO的服务端通信模型:
- 采用BIO通信模型的服务端,通常由一个独立的Acceptor线程负责监听客户端的连接,它接收到客户端连接请求之后为每个客户端创建一个新的线程进行链路处理没处理完成后,通过输出流返回应答给客户端,线程销毁。即典型的一请求一应答通宵模型。
特点:
- 缺乏弹性伸缩能力,服务端的线程个数和客户端并发访问数呈 1:1 的正比关系。
示例:
- Server:
package com.anxpp.io.calculator.bio; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; /** * BIO服务端源码 * @author yangtao__anxpp.com * @version 1.0 */ public final class ServerNormal { // 默认的端口号 private static int DEFAULT_PORT = 12345; // 单例的ServerSocket private static ServerSocket server; //根据传入参数设置监听端口,如果没有参数调用以下方法并使用默认值 public static void start() throws IOException{ //使用默认值 start(DEFAULT_PORT); } // 这个方法不会被大量并发访问,不太需要考虑效率,直接进行方法同步就行了 public synchronized static void start(int port) throws IOException{ if(server != null) return; try{ // 通过构造函数创建ServerSocket // 如果端口合法且空闲,服务端就监听成功 server = new ServerSocket(port); System.out.println("服务器已启动,端口号:" + port); //通过无线循环监听客户端连接 //如果没有客户端接入,将阻塞在accept操作上。 while(true){ Socket socket = server.accept(); //当有新的客户端接入时,会执行下面的代码 //然后创建一个新的线程处理这条Socket链路 new Thread(new ServerHandler(socket)).start(); } }finally{ //一些必要的清理工作 if(server != null){ System.out.println("服务器已关闭。"); server.close(); server = null; } } } }
package com.anxpp.io.calculator.bio; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.net.Socket; import com.anxpp.io.utils.Calculator; /** * 客户端线程 * @author yangtao__anxpp.com * 用于处理一个客户端的Socket链路 */ public class ServerHandler implements Runnable{ private Socket socket; public ServerHandler(Socket socket) { this.socket = socket; } @Override public void run() { BufferedReader in = null; PrintWriter out = null; try{ in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); out = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(),true); String expression; String result; while(true){ //通过BufferedReader读取一行 //如果已经读到输入流尾部,返回null,退出循环 //如果得到非空值,就尝试计算结果并返回 if((expression = in.readLine())==null) break; System.out.println("服务器收到消息:" + expression); try{ result = Calculator.cal(expression).toString(); }catch(Exception e){ result = "计算错误:" + e.getMessage(); } out.println(result); } }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ //一些必要的清理工作 if(in != null){ try { in.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } in = null; } if(out != null){ out.close(); out = null; } if(socket != null){ try { socket.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } socket = null; } } } }
- Client:
package com.anxpp.io.calculator.bio; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.PrintWriter; import java.net.Socket; /** * 阻塞式I/O创建的客户端 * @author yangtao__anxpp.com * @version 1.0 */ public class Client { // 默认的端口号 private static int DEFAULT_SERVER_PORT = 12345; private static String DEFAULT_SERVER_IP = "127.0.0.1"; public static void send(String expression){ send(DEFAULT_SERVER_PORT,expression); } public static void send(int port,String expression){ System.out.println("算术表达式为:" + expression); Socket socket = null; BufferedReader in = null; PrintWriter out = null; try{ socket = new Socket(DEFAULT_SERVER_IP,port); in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream())); out = new PrintWriter(socket.getOutputStream(),true); out.println(expression); System.out.println("___结果为:" + in.readLine()); }catch(Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); }finally{ // 必要的清理工作 if(in != null){ try { in.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } in = null; } if(out != null){ out.close(); out = null; } if(socket != null){ try { socket.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } socket = null; } } } }
- 测试代码:
package com.anxpp.io.calculator.bio; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.Random; /** * 测试方法 * @author yangtao__anxpp.com * @version 1.0 */ public class Test { // 测试主方法 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // 运行服务器 new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { ServerBetter.start(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }).start(); // 避免客户端先于服务器启动前执行代码 Thread.sleep(100); // 运行客户端 char operators[] = {'+','-','*','/'}; Random random = new Random(System.currentTimeMillis()); new Thread(new Runnable() { @SuppressWarnings("static-access") @Override public void run() { while(true){ //随机产生算术表达式 String expression = random.nextInt(10)+""+operators[random.nextInt(4)]+(random.nextInt(10)+1); Client.send(expression); try { Thread.currentThread().sleep(random.nextInt(1000)); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } }).start(); } }
- 运行结果:
服务器已启动,端口号:12345 算术表达式为:4-2 服务器收到消息:4-2 ___结果为:2 算术表达式为:5-10 服务器收到消息:5-10 ___结果为:-5 算术表达式为:0-9 服务器收到消息:0-9 ___结果为:-9 算术表达式为:0+6 服务器收到消息:0+6 ___结果为:6 算术表达式为:1/6 服务器收到消息:1/6 ___结果为:0.16666666666666666 ...
伪异步I/O编程
为了改进以上一连接一线程的模型,我们可以使用线程池来管理这些线程,实现 1 个或多个线程处理 N 个客户端的模型(但是底层还是使用的同步阻塞I/O),通常被称为“伪异步I/O模型“。
- 只需要Server端新建线程交给线程池管理即可:【替换上节的“ServerNormal”】
package com.anxpp.io.calculator.bio; import java.io.IOException; import java.net.ServerSocket; import java.net.Socket; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; /** * BIO服务端源码__伪异步I/O * @author yangtao__anxpp.com * @version 1.0 */ public final class ServerBetter { // 默认的端口号 private static int DEFAULT_PORT = 12345; // 单例的ServerSocket private static ServerSocket server; // 线程池【懒汉式的单例】 private static ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(60); // 根据传入参数设置监听端口,如果没有参数调用以下方法并使用默认值 public static void start() throws IOException{ //使用默认值 start(DEFAULT_PORT); } //这个方法不会被大量并发访问,不太需要考虑效率,直接进行方法同步就行了 public synchronized static void start(int port) throws IOException{ if(server != null) return; try{ // 通过构造函数创建ServerSocket // 如果端口合法且空闲,服务端就监听成功 server = new ServerSocket(port); System.out.println("服务器已启动,端口号:" + port); // 通过无线循环监听客户端连接 // 如果没有客户端接入,将阻塞在accept操作上。 while(true){ Socket socket = server.accept(); //当有新的客户端接入时,会执行下面的代码 //然后创建一个新的线程处理这条Socket链路 executorService.execute(new ServerHandler(socket)); } }finally{ //一些必要的清理工作 if(server != null){ System.out.println("服务器已关闭。"); server.close(); server = null; } } } }
如果使用CachedThreadPool线程池(不限制线程数量),其实除了能自动帮我们管理线程(复用),看起来也就像是 1:1 的 客户端:线程数 模型,
而使用FixedThreadPool就有效的控制了线程的最大数量,保证了系统有限的资源的控制,实现了 N:M 的伪异步I/O模型。
JavaNIO的BIO编程
NIO(non-blocking IO)
AIO(asynchronous IO)
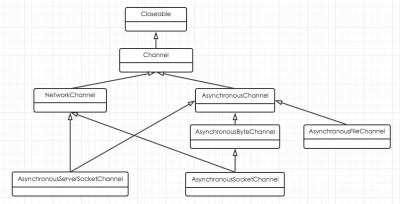
AIO 是 Java 1.7 之后引入的包,是 NIO 的升级版本,新增了提异步非阻塞的 IO 操作方式,所以人们叫它 AIO(Asynchronous IO),异步 IO 是基于事件和回调机制实现的,也就是应用操作之后会直接返回,不会堵塞在那里,当后台处理完成,操作系统会执行回调通知相应的线程进行后续的操作。
在Java 7中增加了asynchronous IO,具体结构和实现类框架如下: