SpringMVC:高级应用
Validation
对提交的请求数据进行检验。
依赖包
- hibernate-validator-4.3.0.Final.jar
- jboss-logging-3.1.0.CR2.jar
- validation-api-1.0.0.GA.jar
配置validator
springmvc.xml
| 使用<mvc:annotation-driven> | 使用HandlerAdapter |
|---|---|
<mvc:annotation-driven validator="validator"></mvc:annotation-driven>
|
<!-- 注解适配器 -->
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter">
<property name="webBindingInitializer" ref="customBinder"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 自定义webBinder -->
<bean id="customBinder"
class="org.springframework.web.bind.support.ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer">
<property name="validator" ref="validator" />
</bean>
|
<!-- 校验器 -->
<bean id="validator" class="org.springframework.validation.beanvalidation.LocalValidatorFactoryBean">
<!-- hibernate校验器-->
<property name="providerClass" value="org.hibernate.validator.HibernateValidator" />
<!-- 指定校验使用的资源文件,在文件中配置校验错误信息,如果不指定则默认使用classpath下的ValidationMessages.properties -->
<property name="validationMessageSource" ref="messageSource" />
</bean>
<!-- 校验错误信息配置文件 -->
<bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ReloadableResourceBundleMessageSource">
<!-- 资源文件名-->
<property name="basenames">
<list>
<value>classpath:CustomValidationMessages</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- 资源文件编码格式 -->
<!-- <property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8"></property> -->
<property name="fileEncodings" value="UTF-8" />
<!-- 对资源文件内容缓存时间,单位秒 -->
<property name="cacheSeconds" value="120" />
</bean>
| |
CustomValidationMessages.properties
位置参考<value>classpath:CustomValidationMessages</value>,内容如:
#添加校验错误提交信息
items.name.length.error=请输入1到30个字符的商品名称
items.createtime.isNUll=请输入商品的生产日期
item.price.isNull=test,价格不能为空
items.message.test=校验信息配置测试文字
使用validator
添加验证规则
在pojo的属性之上添加验证规则:@NotNull(message="{item.price.isNull}",groups= {ValidGroup1.class}),其中:
@NotNull:校验名称;message="{item.price.isNull}":错误信息(配置于“CustomValidationMessages.properties”);groups= {ValidGroup1.class}:此校验所属的分组;
public class Items {
private Integer id;
//校验名称在1到30字符中间
//message是提示校验出错显示的信息
//groups:此校验属于哪个分组,groups可以定义多个分组
@Size(min=1,max=30,message="{items.message.test}",groups={ValidGroup1.class})
private String name;
@NotNull(message="{item.price.isNull}",groups= {ValidGroup1.class})
private Float price;
private String pic;
//非空校验
@NotNull(message="{items.createtime.isNUll}",groups= {ValidGroup1.class})
private Date createtime;
private String detail;
//get、set、toString...
}
错误消息文件
验证规则中配置的message="{item.price.isNull}",对应于“CustomValidationMessages.properties”中的信息:
#添加校验错误提交信息
items.name.length.error=请输入1到30个字符的商品名称
items.createtime.isNUll=请输入商品的生产日期
item.price.isNull=test,价格不能为空
items.message.test=校验信息配置测试文字
- 如果在eclipse中编辑properties文件无法看到中文则参考“Eclipse开发环境配置-indigo.docx”添加propedit插件。【???】
捕获错误
在Controller的方法形参前添加@Validated来在参数绑定时进行校验,并将校验信息写入BindingResult中:
- 在要校验的pojo后边添加
BingdingResult; - 一个
BindingResult对应一个pojo;
// 商品信息修改提交
// 在需要校验的pojo前边添加@Validated,在需要校验的pojo后边添加BindingResult
// bindingResult接收校验出错信息
// 注意:@Validated和BindingResult bindingResult是配对出现,并且形参顺序是固定的(一前一后)。
// value={ValidGroup1.class}指定使用ValidGroup1分组的 校验
// @ModelAttribute可以指定pojo回显到页面在request中的key
@RequestMapping("/editItemsSubmit")
public String editItemsSubmit(
Model model,
HttpServletRequest request,
Integer id,
@ModelAttribute("items") @Validated(value = { ValidGroup1.class}) ItemsCustom itemsCustom,
BindingResult bindingResult,
MultipartFile items_pic//接收商品图片
) throws Exception {
// 获取校验错误信息
if (bindingResult.hasErrors()) {
// 输出错误信息
List<ObjectError> allErrors = bindingResult.getAllErrors();
for (ObjectError objectError : allErrors) {
// 输出错误信息
System.out.println(objectError.getDefaultMessage());
}
// 将错误信息传到页面
model.addAttribute("allErrors", allErrors);
// 可以直接使用model将提交pojo回显到页面
model.addAttribute("items", itemsCustom);
// 出错重新到商品修改页面
return "items/editItems";
}
//原始名称
String originalFilename = items_pic.getOriginalFilename();
//上传图片
if(items_pic!=null && originalFilename!=null && originalFilename.length()>0){
//存储图片的物理路径
String pic_path = "F:\\develop\\upload\\temp\\";
//新的图片名称
String newFileName = UUID.randomUUID() + originalFilename.substring(originalFilename.lastIndexOf("."));
//新图片
File newFile = new File(pic_path+newFileName);
//将内存中的数据写入磁盘
items_pic.transferTo(newFile);
//将新图片名称写到itemsCustom中
itemsCustom.setPic(newFileName);
}
// 调用service更新商品信息,页面需要将商品信息传到此方法
itemsService.updateItems(id, itemsCustom);
return "success";
}
错误回显
在捕获错误后,页面需要显示错误信息。
如:
- 页头:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" <%@ taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" %>
- 在需要显示错误信息地方:
<spring:hasBindErrors name="item"> <c:forEach items="${errors.allErrors}" var="error"> ${error.defaultMessage }<br/> </c:forEach> </spring:hasBindErrors>
<spring:hasBindErrors name="item">表示如果item参数绑定校验错误下边显示错误信息。
或,如:【???????????】
- Controller:
if(bindingResult.hasErrors()){ model.addAttribute("errors", bindingResult); }
- 在需要显示错误信息地方:
<c:forEach items="${errors.allErrors}" var="error"> ${error.defaultMessage }<br/> </c:forEach>
分组校验
如果两处校验使用同一个Items类则可以设定校验分组,通过分组校验可以对每处的校验个性化。
定义分组
分组就是一个标识,可以使用一个空接口来进行分组定义。
package cn.itcast.ssm.controller.validation;
public interface ValidGroup1 {
//接口中不需要定义任何方法,仅是对不同的校验规则进行分组
//此分组只校验商品名称长度
}
package cn.itcast.ssm.controller.validation;
public interface ValidGroup2 {
//接口中不需要定义任何方法,仅是对不同的校验规则进行分组
//此分组只校验xxxxxx
}
指定分组
在pojo的校验规则中使用groups= {ValidGroup1.class}来指定所属的分组。
@Size(min=1,max=30,message="{items.message.test}",groups={ValidGroup1.class})
private String name;
@NotNull(message="{item.price.isNull}",groups= {ValidGroup1.class})
private Float price;
@NotNull(message="{items.createtime.isNUll}",groups= {ValidGroup1.class})
private Date createtime;
使用分组校验
在Controller中使用@Validated(value={ValidGroup1.class})来使用ValidGroup1分组的检验规则。
// 商品修改提交
@RequestMapping("/editItemSubmit")
public String editItemSubmit(
@Validated(value={ValidGroup1.class}) @ModelAttribute("item") Items items,
BindingResult result,
@RequestParam("pictureFile") MultipartFile[] pictureFile,
Model model) throws Exception {
...
}
- 也可以使用逗号分隔来指定多个分组:
@Validated(value={ValidGroup1.class,ValidGroup2.class })
校验注解
| 校验 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| @Null | 被注释的元素必须为 null |
| @NotNull | 被注释的元素必须不为 null |
| @AssertTrue | 被注释的元素必须为 true |
| @AssertFalse | 被注释的元素必须为 false |
| @Min(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
| @Max(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
| @DecimalMin(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
| @DecimalMax(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
| @Size(max=, min=) | 被注释的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内 |
| @Digits (integer, fraction) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内 |
| @Past | 被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期 |
| @Future | 被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期 |
| @Pattern(regex=,flag=) | 被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式 |
| Hibernate Validator 附加的 constraint | |
| @NotBlank(message =) | 验证字符串非null,且长度必须大于0 |
| 被注释的元素必须是电子邮箱地址 | |
| @Length(min=,max=) | 被注释的字符串的大小必须在指定的范围内 |
| @NotEmpty | 被注释的字符串的必须非空 |
| @Range(min=,max=,message=) | 被注释的元素必须在合适的范围内 |
数据回显
数据回显:表单提交失败,回到表单填写页面时,将原提交的数据重新显示在页面中。
简单类型
简单的数据类型的回显,使用Model将传入的参数添加到request域即可。
@RequestMapping(value="/editItems",method={RequestMethod.GET})
public String editItems(Model model,Integer id)throws Exception{
//传入的id重新放到request域
model.addAttribute("id", id);
...
}
pojo类型
- 默认回显:pojo数据传入controller方法后,springmvc自动将pojo数据放到request域,;
@RequestMapping("/editItemSubmit") public String editItemSubmit(Integer id,ItemsCustom itemsCustom)throws Exception{}
<tr> <td>商品名称</td> <td><input type="text" name="name" value="${itemsCustom.name}"/></td> </tr> <tr> <td>商品价格</td> <td><input type="text" name="price" value="${itemsCustom.price}"/></td> </tr>
- 仅request的key等于pojo类型(首字母小写)时;
- 相当于调用下边的代码
model.addAttribute("itemsCustom", itemsCustom);
- 使用@ModelAttribute将方法的返回值传到页面;
@RequestMapping("/editItemSubmit") public String editItemSubmit(Integer id,@ModelAttribute("item") ItemsCustom itemsCustom){}
<tr> <td>商品名称</td> <td><input type="text" name="name" value="${item.name}"/></td> </tr> <tr> <td>商品价格</td> <td><input type="text" name="price" value="${item.price}"/></td> </tr>
- 最简单的方法是使用model,而不用@ModelAttribute;
@RequestMapping("/editItemSubmit") public String editItemSubmit(Model model,ItemsCustom itemsCustom){ // 可以直接使用model将提交pojo回显到页面 model.addAttribute("items", itemsCustom); }
<tr> <td>商品名称</td> <td><input type="text" name="name" value="${item.name}"/></td> </tr> <tr> <td>商品价格</td> <td><input type="text" name="price" value="${item.price}"/></td> </tr>
- 通过形参中的model将model数据传到页面,相当于modelAndView.addObject方法;
方法返回值
可以将方法返回值暴露为模型数据,传到视图页面。
如,将获取商品类型的方法的返回值,传递到页面:
// 商品分类
//itemtypes表示最终将方法返回值放在request中的key
@ModelAttribute("itemtypes")
public Map<String, String> getItemTypes() {
Map<String, String> itemTypes = new HashMap<String, String>();
itemTypes.put("101", "数码");
itemTypes.put("102", "母婴");
return itemTypes;
}
<select name="itemtype">
<c:forEach items="${itemtypes}" var="itemtype">
<option value="${itemtype.key}">${itemtype.value}</option>
</c:forEach>
</select>
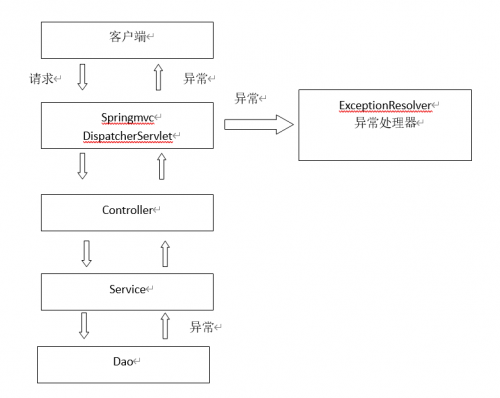
异常处理器
springmvc在处理请求过程中出现异常信息交由异常处理器进行处理,自定义异常处理器可以实现一个系统的异常处理逻辑。
处理思路:
- 系统的dao、service、controller出现都通过throws Exception向上抛出,最后由springmvc前端控制器交由异常处理器进行异常处理。
自定义异常
为了区别不同的异常通常根据异常类型自定义异常类,这里我们创建一个自定义系统异常,如果controller、service、dao抛出此类异常说明是系统预期处理的异常信息。
public class CustomException extends Exception {
/** serialVersionUID*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = -5212079010855161498L;
public CustomException(String message){
super(message);
this.message = message;
}
//异常信息
private String message;
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}
自定义异常处理器
public class CustomExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
@Override
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
CustomException customException = null;
//如果抛出的是系统自定义异常则直接转换
if(ex instanceof CustomException){
customException = (CustomException)ex;
}else{
//如果抛出的不是系统自定义异常则重新构造一个未知错误异常。
customException = new CustomException("未知错误,请与系统管理 员联系!");
}
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("message", customException.getMessage());
modelAndView.setViewName("error");
return modelAndView;
}
}
错误页面
error.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" prefix="fmt"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8">
<title>错误页面</title>
</head>
<body>
您的操作出现错误如下:<br/>
${message }
</body>
</html>
配置异常处理器
springmvc.xml中添加
<!-- 异常处理器 -->
<bean id="handlerExceptionResolver" class="cn.itcast.ssm.controller.exceptionResolver.CustomExceptionResolver"/>
异常测试
如:修改controller方法“editItem”,调用service查询商品信息,如果商品信息为空则抛出异常。
// 调用service查询商品信息
Items item = itemService.findItemById(id);
if(item == null){
throw new CustomException("商品信息不存在!");
}
上传图片
依赖包
- commons-fileupload-1.2.2.jar
- commons-io-2.4.jar
配置上传目录
在服务器中(如:tomcat、nginx)上配置图片虚拟目录:
- tomcat:
- 在配置文件“conf/server.xml”中添加:
<Context docBase="F:\develop\upload\temp" path="/pic" reloadable="false"/> - 或者,通过eclipse配置:
- 访问http://localhost:8080/pic即可访问F:\develop\upload\temp下的图片。
- 在配置文件“conf/server.xml”中添加:
配置解析器
springmvc.xml中添加:
<!-- 文件上传 -->
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<!-- 设置上传文件的最大尺寸为5MB -->
<property name="maxUploadSize">
<value>5242880</value>
</property>
</bean>
上传测试
- controller:
//商品修改提交 @RequestMapping("/editItemSubmit") public String editItemSubmit(Items items, MultipartFile pictureFile)throws Exception{ //原始文件名称 String pictureFile_name = pictureFile.getOriginalFilename(); if(pictureFile!=null && pictureFile_name!=null && pictureFile_name.length()>0){ //存储图片的物理路径 String pic_path = "F:\\develop\\upload\\temp\\"; //新文件名称 String newFileName = UUID.randomUUID().toString()+pictureFile_name.substring(pictureFile_name.lastIndexOf(".")); //上传图片 File uploadPic = new java.io.File(pic_path+newFileName); if(!uploadPic.exists()){ uploadPic.mkdirs(); } //向磁盘写文件 pictureFile.transferTo(uploadPic); } ... }
- view:
<form id="itemForm" action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/items/editItemsSubmit.action" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data"> <input type="hidden" name="id" value="${items.id}"/> 修改商品信息: <table width="100%" border=1> ... <tr> <td>商品图片</td> <td> <c:if test="${items.pic!=null}"> <img src="/pic/${items.pic}" width=100 height=100/> <br/> </c:if> <input type="file" name="pictureFile"/> </td> </tr> ... </table> </form>
- form添加
enctype="multipart/form-data"; - file的name与controller形参一致(为pictureFile);
json数据交互
依赖包
Springmvc默认用MappingJacksonHttpMessageConverter对json数据进行转换,需要加入jackson的包:
- jackson-core-asl-1.9.11.jar
- jackson-mapper-asl-1.9.11.jar
配置转换器
在注解适配器中加入messageConverters:
<!--注解适配器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter">
<property name="messageConverters">
<list>
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJacksonHttpMessageConverter"></bean>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
- 使用
<mvc:annotation-driven />时无需配置以上内容。
@RequestBody
@RequestBody注解用于读取http请求的内容(字符串),通过springmvc提供的HttpMessageConverter接口将读到的内容转换为json、xml等格式的数据并绑定到controller方法的参数上。
@RequestBody将请求的json串转成pojo对象,进行参数绑定。
@ResponseBody
@ResponseBody注解用于将Controller的方法返回的对象,通过HttpMessageConverter接口转换为指定格式的数据(如:json、xml等),通过Response响应给客户端。
@ResponseBody将pojo对象转成json,进行输出。
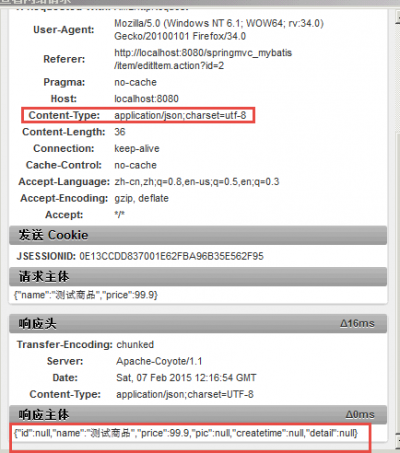
请求json,响应json
controller:
// 商品修改提交json信息,响应json信息
@RequestMapping("/editItemSubmit_RequestJson")
public @ResponseBody Items editItemSubmit_RequestJson(@RequestBody Items items) throws Exception {
System.out.println(items);
//itemService.saveItem(items);
return items;
}
view:js方法
需引入jquery:<script type="text/javascript" src="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/js/jquery-1.4.4.min.js"></script>
//请求json响应json
function request_json(){
$.ajax({
type:"post",
url:"${pageContext.request.contextPath }/item/editItemSubmit_RequestJson.action",
contentType:"application/json;charset=utf-8",
data:'{"name":"测试商品","price":99.9}',
success:function(data){
alert(data);
}
});
}
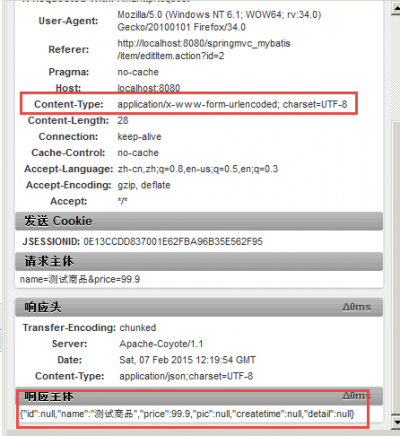
请求key/value,响应json
- 实际开发中常用,请求key/value数据,响应json结果,方便客户端对结果进行解析。
- 表单默认请求
application/x-www-form-urlencoded格式的数据即key/value,通常有post和get两种方法。
controller:
// 商品修改提交,提交普通form表单数据,响应json
@RequestMapping("/editItemSubmit_ResponseJson")
public @ResponseBody Items editItemSubmit_ResponseJson(Items items) throws Exception {
System.out.println(items);
//itemService.saveItem(items);
return items;
}
view:js方法
//请求application/x-www-form-urlencoded响应json
function formsubmit(){
var user = "name=测试商品&price=99.9";
alert(user);
$.ajax({
type:'post',//这里改为get也可以正常执行
url:'${pageContext.request.contextPath}/item/ editItemSubmit_RequestJson.action',
//ContentType没指定将默认为:application/x-www-form-urlencoded
data:user,
success:function(data){
alert(data.name);
}
})
}
- 去掉ContentType定义,默认为:application/x-www-form-urlencoded格式
RESTful支持
RESTful,是目前最流行的一种互联网软件架构风格。理解RESTful重点在于理解“Representational State Transfer”(表现层状态转化)。
RESTful的设计原则:
- 使用HTTP动词:GET POST PUT DELETE;
- 无状态连接,服务器端不应保存过多上下文状态,即每个请求都是独立的;
- 为每个资源设置URI;
- 通过XML JSON进行数据传递;
RESTful的实现:
- url规范:
- 非RESTful风格的url:“http://wiki.eijux.com/index.php?title=首页”;
- RESTful风格的url:“http://wiki.eijux.com/首页”;(参见MediaWiki:短链接)
- http方法规范:
- 对资源的删除、添加、更新操作,对应于同一url,和不同的http方法;
- controller通过判断http方法来进行不同的操作;
- http的contentType规范
- 请求时指定contentType(contentType:"application/json;charset=utf-8"),以JSON格式进行数据传递。
DispatcherServlet的rest配置
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring/springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>:所有访问的地址(除jsp之外)都由DispatcherServlet进行解析,可以实现 RESTful风格的url(对于静态资源的解析需要配置不让DispatcherServlet进行解析)。
静态资源访问<mvc:resources>
如果在DispatcherServlet中设置url-pattern为 /则必须对静态资源进行访问处理。
springMVC中使用<mvc:resources mapping="" location="">可以实现对静态资源(如js、css、img)进行映射访问:
- <mvc:resources>由springMVC框架自己处理资源,与容器无关;
- 隐藏了真实路径结构;
- 能访问"WEB-INF"下内容;
- (“/”:表示WebRoot目录)
使用如:
<!--
<mvc:resources location="/js/" mapping="/js/**"/>
<mvc:resources location="/jquery/" mapping="/jquery/**"/>
<mvc:resources location="/img/" mapping="/img/**"/>
<mvc:resources location="/" mapping="/resources/**"></mvc:resources>
-->
<!-- 隐藏真实路径结构 -->
<mvc:resources location="/js/,/jquery/,/WEB-INF/jscript/" mapping="/resources/**"></mvc:resources>
<!-- 访问"WEB-INF"下内容 -->
<mvc:resources location="/WEB-INF/jscript/" mapping="/webJscript/**"></mvc:resources>
URL 模板模式映射
在controller中使用@RequestMapping和@PathVariable来实现url映射:
@RequestMapping(value="/itemsView/{id}"):{×××}为占位符,请求的URL可以是“/viewItems/1”或“/viewItems/2”等;@PathVariable用于将请求URL中的模板变量(×××)映射到功能处理方法的参数上。- 如果RequestMapping中占位符与方法形参名称一致,则@PathVariable不用指定名称(如:“@PathVariable Integer id”)。
//查询商品信息,输出json
///itemsView/{id}里边的{id}表示占位符,通过@PathVariable获取占位符中的参数,
//如果占位符中的名称和形参名一致,在@PathVariable可以不指定名称
@RequestMapping("/itemsView/{id}")
public @ResponseBody ItemsCustom itemsView(@PathVariable("id") Integer id)throws Exception{
//调用service查询商品信息
ItemsCustom itemsCustom = itemsService.findItemsById(id);
return itemsCustom;
}
@ResponseBody表示以json响应。
拦截器
Spring Web MVC 的处理器拦截器类似于Servlet 开发中的过滤器Filter,用于对处理器进行预处理和后处理。
- 本质也是AOP(面向切面编程),即符合横切关注点的所有功能都可以放入拦截器实现;
- HandlerInterceptor在springMVC环境使用,而Filter在Servlet规范中通用;
拦截器定义
定义拦截器,实现HandlerInterceptor接口(或继承HandlerInterceptorAdapter适配器类)。接口中提供三个方法:
preHandle:postHandle:afterCompletion:
Public class HandlerInterceptor1 implements HandlerInterceptor{
/**
* controller执行前调用此方法
* 返回true表示继续执行,返回false中止执行
* 应用场景:登录校验、权限拦截等
*/
@Override
Public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return false;
}
/**
* controller执行后,返回modelAndView之前执行
* 应用场景:对模型数据进行加工处理,比如将公用的模型数据(比如菜单导航)在这里传到视图,也可以在这里统一指定视图
*/
@Override
Public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, Object handler,
ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
/**
* controller执行后且视图返回后调用此方法
* 这里可得到执行controller时的异常信息
* 应用场景:统一异常处理,统一日志处理,资源清理等
*/
@Override
Public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex)
throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
如果实现HandlerInterceptor接口的话,三个方法必须实现。而对于只需要其中某个方法时,可以采用继承抽象类HandlerInterceptorAdapter(适配器模式的实现)的方式:
public class ManualInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {
...
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
if(...)){
...
return true;
}
return true;
}
}
关于HandlerInterceptorAdapter:
- public abstract class HandlerInterceptorAdapter implements AsyncHandlerInterceptor
- 抽象类(HandlerInterceptorAdapter)实现了接口(AsyncHandlerInterceptor):使普通类可以只实现接口中的部分方法,避免代码冗余
- public interface AsyncHandlerInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptor
- 接口(AsyncHandlerInterceptor)继承了接口(HandlerInterceptor)
- public interface HandlerInterceptor
package org.springframework.web.servlet.handler;
...
public abstract class HandlerInterceptorAdapter implements AsyncHandlerInterceptor {
/**
* This implementation always returns {@code true}.
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return true;
}
/**
* This implementation is empty.
*/
@Override
public void postHandle(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView)
throws Exception {
}
/**
* This implementation is empty.
*/
@Override
public void afterCompletion(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex)
throws Exception {
}
/**
* This implementation is empty.
*/
@Override
public void afterConcurrentHandlingStarted(
HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
}
}
拦截器配置
| 配置HandlerMapping拦截器 | 全局拦截器 |
|---|---|
<!-- 添加拦截器到HandlerMapping -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping">
<property name="interceptors">
<list>
<ref bean="handlerInterceptor1"/>
<ref bean="handlerInterceptor2"/>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 注册拦截器 -->
<bean id="handlerInterceptor1" class="springmvc.intercapter.HandlerInterceptor1"/>
<bean id="handlerInterceptor2" class="springmvc.intercapter.HandlerInterceptor2"/>
|
<!--拦截器 -->
<mvc:interceptors>
<!--多个拦截器,顺序执行 -->
<!-- /**表示所有url包括子url路径 -->
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<bean class="cn.itcast.springmvc.filter.HandlerInterceptor1"></bean>
</mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<bean class="cn.itcast.springmvc.filter.HandlerInterceptor2"></bean>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
|
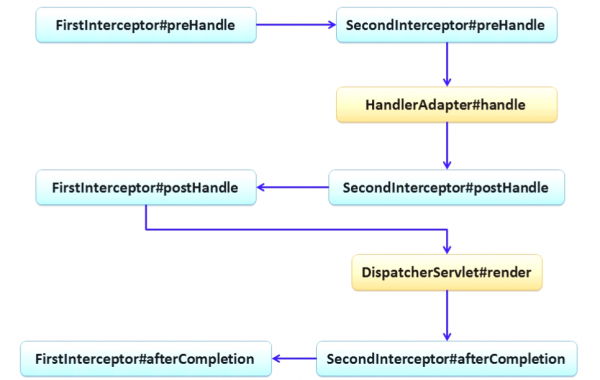
拦截器链执行流程
SpringMVC 中的Interceptor 是链式的调用的,在一个应用中或者说是在一个请求中可以同时存在多个Interceptor 。每个Interceptor 的调用会依据它的声明顺序依次执行,
拦截器执行流程测试:
| Interceptor1、Interceptor2均放行 | Interceptor1放行、Interceptor2不放行 | Interceptor1不放行、Interceptor2不放行 |
|---|---|---|
HandlerInterceptor1...preHandle HandlerInterceptor2...preHandle HandlerInterceptor2...postHandle HandlerInterceptor1...postHandle HandlerInterceptor2...afterCompletion HandlerInterceptor1...afterCompletion |
HandlerInterceptor1...preHandle HandlerInterceptor2...preHandle HandlerInterceptor1...afterCompletion |
HandlerInterceptor1...preHandle |
|
|
|