RabbitMQ:SpringBoot(工作模式)
跳到导航
跳到搜索
关于
无论使用 RabbitMQ 那种工作模式,区别就是使用的交换机(Exchange)类型和路由参数不一样。
- 简单队列、Work模式,底层会使用默认的交换机(Direct交换机);
以下示例,生产者、消费者位于不同项目,所以两个项目都需要:引入Maven依赖、RabbitMQ配置、队列/交换机配置(使用“全注解方式定义队列监听器”则客户端不需要该配置)。
- 根据不同的工作模式,生成者、消费者并都不需要配置队列/交换机;(见:RabbitMQ:Java)
以下,生产者、消费者均省略了“Maven依赖”、“配置文件内容”:
- Maven依赖:
<dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactid> </dependency>
- 目前 Java 操作 RabbitMQ 主要使用 Springboot 的 spring-boot-starter-amqp 包, 其实就是使用 Spring AMQP 操作队列。
- 配置 RabbitMQ:修改application.yml配置。
spring: rabbitmq: # rabbitMQ服务器地址 host: localhost port: 5672 username: guest password: guest
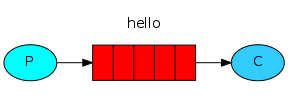
快速入门(简单队列)
Java RabbitMQ最简单的队列模式就是一个生产者和一个消费者。
发送消息
- 配置队列:
- 通过 springboot 的 configuration 类配置队列:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class QueueConfig { @Bean public Queue helloQueue() { // 声明队列, 队列名需要唯一 return new Queue("hello"); } }
- 可以根据业务需要定义多个队列,Queue name(队列名)和 Bean id(此处即方法名)不一样即可。
- 如上,Bean id:“helloQueue”;Queue name:“hello”;
- 发送消息:
- 发送消息需要用到 RabbitTemplate 类,springboot已经帮我们初始化,注入实例即可:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.service; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class SendService { // 注入RabbitTemplate实例 @Autowired private RabbitTemplate template; // 注入前面定义的队列 @Autowired @Qualifier("helloQueue") private Queue helloQueue; // 为了演示,这里使用spring内置的定时任务,定时发送消息(每秒发送一条消息) @Scheduled(fixedDelay = 1000, initialDelay = 1000) public void send() { // 消息内容 String message = "Hello World!"; // 发送消息 // 第一个参数是路由参数,这里使用队列名作为路由参数 // 第二个参数是消息内容,支持任意类型,只要支持序列化 template.convertAndSend(helloQueue.getName(), message); System.out.println("发送消息 '" + message + "'"); } }
- 这里没有直接使用交换机(exchange),底层会使用默认的交换机(Direct交换机???)。
接收消息
- 配置队列:
- 通过 springboot 的 configuration 类配置队列:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class QueueConfig { @Bean public Queue helloQueue() { // 声明队列, 队列名需要唯一 return new Queue("hello"); } }
- 接收消息:
- 接收消息需要用 @RabbitListener(queues = "xxx") 注解指定接受哪个 Queue 的消息:
- “@RabbitListener”注解可以作用在类上,也可以作用在方法上;
- 如果其定义在类上,则需要配合“@RabbitHandler”注解标记由那个类方法执行消息处理。
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.listener; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component // 声明消息监听器,通过queues参数指定监听的队列,需要跟前面的队列名保持一致 @RabbitListener(queues = "hello") public class HelloListener { // 使用RabbitHandler标记消息处理器,用来执行消息处理逻辑 @RabbitHandler public void receive(String msg) { System.out.println("消费者 - 收到消息 '" + msg + "'"); } }
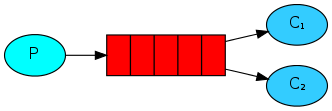
Work模式
Java RabbitMQ Work模式,就是配置多个消费者消费一个队列的消息,可以提高消息的并发处理速度:
接收消息(配置多个消费者)
通过@RabbitListener注解,配置concurrency参数即可实现。
如下,启动10个消费者并发处理消息:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.listener;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
// 声明消息监听器,通过queues参数指定监听的队列
// 关键参数:concurrency 代表当前监听器需要启动多少个消费者,类型是字符串
@RabbitListener(queues = "hello", concurrency = "10")
public class HelloListener {
// 使用RabbitHandler标记消息处理器,用来执行消息处理逻辑
@RabbitHandler
public void receive(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者 - 收到消息 '" + msg + "'");
}
}
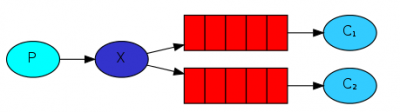
发布订阅模式
Java RabbitMQ发布订阅模式(广播模式、fanout模式),使用的交换机类型为FanoutExchange,就是一个生产者发送的消息会被多个队列的消费者处理:
发送消息
- 配置交换机:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class QueueConfig { // 定义交换机 @Bean public FanoutExchange fanout() { // 参数为交换机名字,不能重复 return new FanoutExchange("tizi365.fanout"); } }
- 发送消息:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.service; import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class SendService { @Autowired private RabbitTemplate template; @Autowired private FanoutExchange fanout; // 为演示,这里使用定时任务,每秒发送一条消息 @Scheduled(fixedDelay = 1000, initialDelay = 1000) public void send() { // 消息内容 String message = "Hello World!"; // 发送消息 // 第一个参数是交换机名字 // 第二个参数是路由参数,fanout交换机会忽略路由参数,所以不用设置 // 第三个参数是消息内容,支持任意类型,只要支持序列化 template.convertAndSend(fanout.getName(), "", message); System.out.println("发送消息 '" + message + "'"); } }
接收消息
- 配置交换机、队列及绑定:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class QueueConfig { // 定义交换机 @Bean public FanoutExchange fanout() { // 参数为交换机名字,不能重复 return new FanoutExchange("tizi365.fanout"); } @Bean public Queue queue1() { // 定义队列1 return new Queue("tizi365.fanout.queue1"); } @Bean public Queue queue2() { // 定义队列2 return new Queue("tizi365.fanout.queue2"); } @Bean public Binding binding1(FanoutExchange fanout, Queue queue1) { // 定义一个绑定关系,将队列1绑定到fanout交换机上 return BindingBuilder.bind(queue1).to(fanout); } @Bean public Binding binding2(FanoutExchange fanout, Queue queue2) { // 定义一个绑定关系,将队列2绑定到fanout交换机上 return BindingBuilder.bind(queue2).to(fanout); } }
- 接收消息:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.listener; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; // 将当前类交给Spring管理 @Component public class DemoListener { // 定义一个监听器,通过queues参数指定监听那个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "tizi365.fanout.queue1") public void receive1(String msg) { System.out.println("收到队列1的消息 = " + msg); } // 定义一个监听器,通过queues参数指定监听那个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "tizi365.fanout.queue2") public void receive2(String msg) { System.out.println("收到队列2的消息 = " + msg); } }
- 每一条消息,都会分发给所有绑定到当前交换机的队列中,消息会被上面的两个方法分别处理。
全注解方式定义队列监听器
直接通过 @RabbitListener 注解的 bindings 参数定义绑定关系、队列、交换机:
- 不再需要消费者项目的配置类定义内容(交换机、队列和绑定关系);
@RabbitListener(bindings = { @QueueBinding( value = @Queue(name = "tizi365.fanout.queue3", durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "tizi365.fanout", durable = "true", type = ExchangeTypes.FANOUT),
// key = ""
)
})
public void receive3(String msg) {
System.out.println("收到队列3的消息 = " + msg);
}
说明:
- QueueBinding 注解:定义队列和交换机的绑定关系:“value”参数用于定义队列,“exchange”用于定义交换机;
- Queue 注解:定义一个队列:“name”参数定义队列名(需要唯一),“durable”参数表示是否需要持久化;
- Exchange 注解:定义一个交换机:“name”参数定义交换机的名字,“type”参数表示交换机的类型;
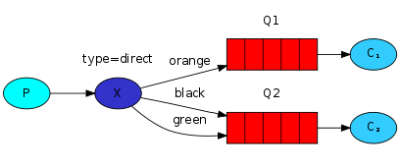
路由模式
Java RabbitMQ路由模式(Direct模式),使用的交换机类型为DirectExchange,跟发布订阅模式的区别就是 Direct 交换机将消息投递到路由参数完全匹配的队列中。
发送消息
- 配置交换机:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.*; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class QueueConfig { @Bean public DirectExchange direct() { // 定义交换机 // 参数为交换机名字,不能重复 return new DirectExchange("tizi365.direct"); } }
- 发送消息:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.service; import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class SendService { @Autowired private RabbitTemplate template; @Autowired private DirectExchange direct; // 为演示,这里使用定时任务,每秒发送一条消息 @Scheduled(fixedDelay = 1000, initialDelay = 1000) public void send() { // 消息内容 String message = "Hello World!"; // 发送消息 // 第一个参数是交换机名字 // 第二个参数是路由参数,direct交换机将消息投递到路由参数匹配tizi365的队列 // 第三个参数是消息内容,支持任意类型,只要支持序列化 template.convertAndSend(direct.getName(), "tizi365", message); System.out.println("发送消息 '" + message + "'"); } }
接收消息
- 配置交换机、队列及绑定:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.*; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class QueueConfig { @Bean public DirectExchange direct() { // 定义交换机 // 参数为交换机名字,不能重复 return new DirectExchange("tizi365.direct"); } @Bean public Queue queue1() { // 定义队列1 return new Queue("tizi365.direct.queue1"); } @Bean public Queue queue2() { // 定义队列2 return new Queue("tizi365.direct.queue2"); } @Bean public Binding binding1(DirectExchange direct, Queue queue1) { // 定义一个绑定关系,将队列1绑定到direct交换机上, 路由参数为:tizi365 // 路由参数匹配tizi365,交换机将消息投递到队列1 return BindingBuilder.bind(queue1).to(direct).with("tizi365"); } @Bean public Binding binding2(DirectExchange direct, Queue queue2) { // 定义一个绑定关系,将队列2绑定到direct交换机上, 路由参数为:baidu // 路由参数匹配baidu,交换机将消息投递到队列2 return BindingBuilder.bind(queue2).to(direct).with("baidu"); } }
- 接受消息:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.listener; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.*; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; // 将当前类交给Spring管理 @Component public class DemoListener { // 定义一个监听器,通过queues参数指定监听那个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "tizi365.direct.queue1") public void receive1(String msg) { System.out.println("收到队列1的消息 = " + msg); } // 定义一个监听器,通过queues参数指定监听那个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "tizi365.direct.queue2") public void receive2(String msg) { System.out.println("收到队列2的消息 = " + msg); } }
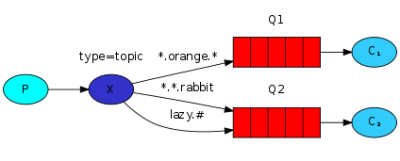
主题模式
Java RabbitMQ 主题模式(Topic模式),使用的交换机类型为TopicExchange,跟路由模式(Direct)的区别就路由参数支持模糊匹配。
- 因为路由匹配比较灵活,所以是比较常用的模式;
发送消息
- 配置交换机:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.*; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class QueueConfig { @Bean public TopicExchange topic() { // 定义交换机 // 参数为交换机名字,不能重复 return new TopicExchange("tizi365.topic"); } }
- 发送信息:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.service; import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange; import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class SendService { @Autowired private RabbitTemplate template; @Autowired private TopicExchange topic; // 为演示,这里使用定时任务,每秒发送一条消息 @Scheduled(fixedDelay = 1000, initialDelay = 1000) public void send() { // 消息内容 String message = "Hello World!"; // 发送消息 // 第一个参数是交换机名字 // 第二个参数是路由参数,topic交换机将消息投递到路由参数匹配的队列 // 第三个参数是消息内容,支持任意类型,只要支持序列化 template.convertAndSend(topic.getName(), "www.tizi365.com", message); System.out.println("发送消息 '" + message + "'"); } }
接收消息
- 配置交换机、队列及绑定:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.*; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class QueueConfig { @Bean public TopicExchange topic() { // 定义交换机 // 参数为交换机名字,不能重复 return new TopicExchange("tizi365.topic"); } @Bean public Queue queue1() { // 定义队列1 return new Queue("tizi365.topic.queue1"); } @Bean public Queue queue2() { // 定义队列2 return new Queue("tizi365.topic.queue2"); } @Bean public Binding binding1(TopicExchange topic, Queue queue1) { // 定义一个绑定关系,将队列1绑定到topic交换机上, 路由参数为:*.tizi365.com return BindingBuilder.bind(queue1).to(topic).with("*.tizi365.com"); } @Bean public Binding binding2(TopicExchange topic, Queue queue2) { // 定义一个绑定关系,将队列2绑定到direct交换机上, 路由参数为:*.baidu.com return BindingBuilder.bind(queue2).to(topic).with("*.baidu.com"); } }
- 支持的通配符:“#”匹配一个或多个单词;“*”:仅匹配一个单词。
- 接受消息:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.listener; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.*; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; // 将当前类交给Spring管理 @Component public class DemoListener { // 定义一个监听器,通过queues参数指定监听那个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "tizi365.topic.queue1") public void receive1(String msg) { System.out.println("收到队列1的消息 = " + msg); } // 定义一个监听器,通过queues参数指定监听那个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "tizi365.topic.queue2") public void receive2(String msg) { System.out.println("收到队列2的消息 = " + msg); } }