RabbitMQ:SpringBoot集成
SpringBoot 集成 RabbitMQ
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
RabbitMQ 配置
(application.yml中)
简单配置:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 127.0.0.1 #ip
port: 5672 #端口
username: guest #账号
password: guest #密码
P.S.:全量配置说明
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 127.0.0.1 #ip
port: 5672 #端口
username: guest #账号
password: guest #密码
virtualHost: #链接的虚拟主机
addresses: 127.0.0.1:5672 #多个以逗号分隔,与host功能一样。
requestedHeartbeat: 60 #指定心跳超时,单位秒,0为不指定;默认60s
publisherConfirms: true #发布确认机制是否启用
publisherReturns: #发布返回是否启用
connectionTimeout: #链接超时。单位ms。0表示无穷大不超时
### ssl相关
ssl:
enabled: #是否支持ssl
keyStore: #指定持有SSL certificate的key store的路径
keyStoreType: #key store类型 默认PKCS12
keyStorePassword: #指定访问key store的密码
trustStore: #指定持有SSL certificates的Trust store
trustStoreType: #默认JKS
trustStorePassword: #访问密码
algorithm: #ssl使用的算法,例如,TLSv1.1
verifyHostname: #是否开启hostname验证
### cache相关
cache:
channel:
size: #缓存中保持的channel数量
checkoutTimeout: #当缓存数量被设置时,从缓存中获取一个channel的超时时间,单位毫秒;如果为0,则总是创建一个新channel
connection:
mode: #连接工厂缓存模式:CHANNEL 和 CONNECTION
size: #缓存的连接数,只有是CONNECTION模式时生效
### listener
listener:
type: #两种类型,SIMPLE,DIRECT
## simple类型
simple:
concurrency: #最小消费者数量
maxConcurrency: #最大的消费者数量
transactionSize: #指定一个事务处理的消息数量,最好是小于等于prefetch的数量
missingQueuesFatal: #是否停止容器当容器中的队列不可用
## 与direct相同配置部分
autoStartup: #是否自动启动容器
acknowledgeMode: #表示消息确认方式,其有三种配置方式,分别是none、manual和auto;默认auto
prefetch: #指定一个请求能处理多少个消息,如果有事务的话,必须大于等于transaction数量
defaultRequeueRejected: #决定被拒绝的消息是否重新入队;默认是true(与参数acknowledge-mode有关系)
idleEventInterval: #container events发布频率,单位ms
##重试机制
retry:
stateless: #有无状态
enabled: #是否开启
maxAttempts: #最大重试次数,默认3
initialInterval: #重试间隔
multiplier: #对于上一次重试的乘数
maxInterval: #最大重试时间间隔
direct:
consumersPerQueue: #每个队列消费者数量
missingQueuesFatal:
#...其余配置看上方公共配置
## template相关
template:
mandatory: #是否启用强制信息;默认false
receiveTimeout: #`receive()`接收方法超时时间
replyTimeout: #`sendAndReceive()`超时时间
exchange: #默认的交换机
routingKey: #默认的路由
defaultReceiveQueue: #默认的接收队列
## retry重试相关
retry:
enabled: #是否开启
maxAttempts: #最大重试次数
initialInterval: #重试间隔
multiplier: #失败间隔乘数
maxInterval: #最大间隔
关键代码
配置类:
/**
* 声明Direct交换机 支持持久化.
*
* @return the exchange
*/
@Bean("directExchange")
public Exchange directExchange() {
return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange("DIRECT_EXCHANGE").durable(true).build();
}
/**
* 声明一个队列 支持持久化.
*
* @return the queue
*/
@Bean("directQueue")
public Queue directQueue() {
return QueueBuilder.durable("DIRECT_QUEUE").build();
}
/**
* 通过绑定键 将指定队列绑定到一个指定的交换机 .
*
* @param queue the queue
* @param exchange the exchange
* @return the binding
*/
@Bean
public Binding directBinding(@Qualifier("directQueue") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("directExchange") Exchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("DIRECT_ROUTING_KEY").noargs();
}
生产者:
// 发送消息
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, "DIRECT_ROUTING_KEY", message);
// 发送消息:为消息设置关联数据???
CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, routeKey, message, correlationData);
// 发送消息:为消息设置过期时间
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, routeKey, message,
new MessagePostProcessor() {
@Override
public Message postProcessMessage(Message message) throws AmqpException {
//给消息设置延迟毫秒值
message.getMessageProperties().setExpiration(String.valueOf(delayTimes));
return message;
}
});
消费者:
// 基础注解,指定queue的名称,可以多个。如果是 simple 不需要交换机的直接写队列名称就好。
// 如果是其他的也想只指定一个queues——name的话,需要配置类配置queue或者其他绑定关系
@RabbitListener(queues = "ly_simple")
@RabbitHandler
public void processSimpleMsg(String message) {
System.out.println("########################received simple" + message);
}
// 如果不想使用配置类,可以直接注解通过 bindings,绑定,spring 会根据注解生成绑定
// ps:如果已有同名称的类。不会覆盖。会影响功能
@RabbitListener(bindings = { @QueueBinding( value = @Queue(value = "ly_direct", durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(value = "ly_direct", type = "direct"),
key = "ly")
})
@RabbitHandler
public void processDirectMsg(String message) {
System.out.println("########################received" + message);
}
集成示例
- maven:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.9.6</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>com.vaadin.external.google</groupId> <artifactId>android-json</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> </dependencies>
- application.yml:
spring: rabbitmq: host: 127.0.0.1 port: 5672 username: spring password: 123456 publisher-confirms: true #支持发布确认 publisher-returns: true #支持发布返回 listener: simple: acknowledge-mode: manual #采用手动应答 concurrency: 1 #指定最小的消费者数量 max-concurrency: 1 #指定最大的消费者数量 retry: enabled: true #是否支持重试
- 配置类:
- 定制模版类、声明交换机、队列、绑定交换机到队列;
@Configuration public class RabbitConfig { @Resource private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; /** * 定制化amqp模版 可根据需要定制多个 * <p> * <p> * 此处为模版类定义 Jackson 消息转换器 * ConfirmCallback 接口用于实现消息发送到 RabbitMQ 交换器后接收 ack 回调 即消息发送到exchange ack * ReturnCallback 接口用于实现消息发送到 RabbitMQ 交换器,但无相应队列与交换器绑定时的回调 即消息发送不到任何一个队列中 ack * * @return the amqp template */ // @Primary @Bean public AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate() { Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RabbitTemplate.class); // 使用jackson 消息转换器 rabbitTemplate.setMessageConverter(new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter()); rabbitTemplate.setEncoding("UTF-8"); // 消息发送失败返回到队列中,yml需要配置 publisher-returns: true rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true); rabbitTemplate.setReturnCallback((message, replyCode, replyText, exchange, routingKey) -> { String correlationId = message.getMessageProperties().getCorrelationIdString(); log.debug("消息:{} 发送失败, 应答码:{} 原因:{} 交换机: {} 路由键: {}", correlationId, replyCode, replyText, exchange, routingKey); }); // 消息确认,yml需要配置 publisher-confirms: true rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback((correlationData, ack, cause) -> { if (ack) { log.debug("消息发送到exchange成功,id: {}", correlationData.getId()); } else { log.debug("消息发送到exchange失败,原因: {}", cause); } }); return rabbitTemplate; } /* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------Direct exchange test--------------------------------------------------------------------------- */ /** * 声明Direct交换机 支持持久化. * * @return the exchange */ @Bean("directExchange") public Exchange directExchange() { return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange("DIRECT_EXCHANGE").durable(true).build(); } /** * 声明一个队列 支持持久化. * * @return the queue */ @Bean("directQueue") public Queue directQueue() { return QueueBuilder.durable("DIRECT_QUEUE").build(); } /** * 通过绑定键 将指定队列绑定到一个指定的交换机 . * * @param queue the queue * @param exchange the exchange * @return the binding */ @Bean public Binding directBinding(@Qualifier("directQueue") Queue queue, @Qualifier("directExchange") Exchange exchange) { return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("DIRECT_ROUTING_KEY").noargs(); } /* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------Fanout exchange test--------------------------------------------------------------------------- */ /** * 声明 fanout 交换机. * * @return the exchange */ @Bean("fanoutExchange") public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() { return (FanoutExchange) ExchangeBuilder.fanoutExchange("FANOUT_EXCHANGE").durable(true).build(); } /** * Fanout queue A. * * @return the queue */ @Bean("fanoutQueueA") public Queue fanoutQueueA() { return QueueBuilder.durable("FANOUT_QUEUE_A").build(); } /** * Fanout queue B . * * @return the queue */ @Bean("fanoutQueueB") public Queue fanoutQueueB() { return QueueBuilder.durable("FANOUT_QUEUE_B").build(); } /** * 绑定队列A 到Fanout 交换机. * * @param queue the queue * @param fanoutExchange the fanout exchange * @return the binding */ @Bean public Binding bindingA(@Qualifier("fanoutQueueA") Queue queue, @Qualifier("fanoutExchange") FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) { return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(fanoutExchange); } /** * 绑定队列B 到Fanout 交换机. * * @param queue the queue * @param fanoutExchange the fanout exchange * @return the binding */ @Bean public Binding bindingB(@Qualifier("fanoutQueueB") Queue queue, @Qualifier("fanoutExchange") FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) { return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(fanoutExchange); } }
- 生产者:
@Service public class SenderService { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass()); @Resource private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; /** * 测试广播模式. * * @param p the p * @return the response entity */ public void broadcast(String p) { CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData(UUID.randomUUID().toString()); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("FANOUT_EXCHANGE", "", p, correlationData); } /** * 测试Direct模式. * * @param p the p * @return the response entity */ public void direct(String p) { CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData(UUID.randomUUID().toString()); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("DIRECT_EXCHANGE", "DIRECT_ROUTING_KEY", p, correlationData); } }
- 消费者:
@Component public class Receiver { private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Receiver.class); /** * FANOUT广播队列监听一. * * @param message the message * @param channel the channel * @throws IOException the io exception 这里异常需要处理 */ @RabbitListener(queues = {"FANOUT_QUEUE_A"}) public void on(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException { channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), true); log.debug("FANOUT_QUEUE_A " + new String(message.getBody())); } /** * FANOUT广播队列监听二. * * @param message the message * @param channel the channel * @throws IOException the io exception 这里异常需要处理 */ @RabbitListener(queues = {"FANOUT_QUEUE_B"}) public void t(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException { channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), true); log.debug("FANOUT_QUEUE_B " + new String(message.getBody())); } /** * DIRECT模式. * * @param message the message * @param channel the channel * @throws IOException the io exception 这里异常需要处理 */ @RabbitListener(queues = {"DIRECT_QUEUE"}) public void message(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException { channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), true); log.debug("DIRECT " + new String(message.getBody())); } }
工作模式
无论使用 RabbitMQ 那种工作模式,区别就是使用的交换机(Exchange)类型和路由参数不一样。
- 简单队列、Work模式,底层会使用默认的交换机(Direct交换机);
以下示例,生产者、消费者位于不同项目,所以两个项目都需要:引入Maven依赖、RabbitMQ配置、队列/交换机配置(使用“全注解方式定义队列监听器”则客户端不需要该配置)。
- 根据不同的工作模式,生成者、消费者并都不需要配置队列/交换机;(见:RabbitMQ:Java)
以下,生产者、消费者均省略了“Maven依赖”、“配置文件内容”:
- Maven依赖:
<dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactid> </dependency>
- 目前 Java 操作 RabbitMQ 主要使用 Springboot 的 spring-boot-starter-amqp 包, 其实就是使用 Spring AMQP 操作队列。
- 配置 RabbitMQ:修改application.yml配置。
spring: rabbitmq: # rabbitMQ服务器地址 host: localhost port: 5672 username: guest password: guest
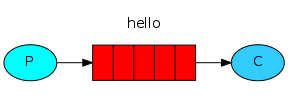
快速入门(简单队列)
Java RabbitMQ最简单的队列模式就是一个生产者和一个消费者。
发送消息
- 配置队列:
- 通过 springboot 的 configuration 类配置队列:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class QueueConfig { @Bean public Queue helloQueue() { // 声明队列, 队列名需要唯一 return new Queue("hello"); } }
- 可以根据业务需要定义多个队列,Queue name(队列名)和 Bean id(此处即方法名)不一样即可。
- 如上,Bean id:“helloQueue”;Queue name:“hello”;
- 发送消息:
- 发送消息需要用到 RabbitTemplate 类,springboot已经帮我们初始化,注入实例即可:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.service; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class SendService { // 注入RabbitTemplate实例 @Autowired private RabbitTemplate template; // 注入前面定义的队列 @Autowired @Qualifier("helloQueue") private Queue helloQueue; // 为了演示,这里使用spring内置的定时任务,定时发送消息(每秒发送一条消息) @Scheduled(fixedDelay = 1000, initialDelay = 1000) public void send() { // 消息内容 String message = "Hello World!"; // 发送消息 // 第一个参数是路由参数,这里使用队列名作为路由参数 // 第二个参数是消息内容,支持任意类型,只要支持序列化 template.convertAndSend(helloQueue.getName(), message); System.out.println("发送消息 '" + message + "'"); } }
- 这里没有直接使用交换机(exchange),底层会使用默认的交换机(Direct交换机???)。
接收消息
- 配置队列:
- 通过 springboot 的 configuration 类配置队列:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class QueueConfig { @Bean public Queue helloQueue() { // 声明队列, 队列名需要唯一 return new Queue("hello"); } }
- 接收消息:
- 接收消息需要用 @RabbitListener(queues = "xxx") 注解指定接受哪个 Queue 的消息:
- “@RabbitListener”注解可以作用在类上,也可以作用在方法上;
- 如果其定义在类上,则需要配合“@RabbitHandler”注解标记由那个类方法执行消息处理。
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.listener; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component // 声明消息监听器,通过queues参数指定监听的队列,需要跟前面的队列名保持一致 @RabbitListener(queues = "hello") public class HelloListener { // 使用RabbitHandler标记消息处理器,用来执行消息处理逻辑 @RabbitHandler public void receive(String msg) { System.out.println("消费者 - 收到消息 '" + msg + "'"); } }
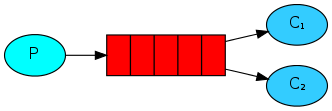
Work模式
Java RabbitMQ Work模式,就是配置多个消费者消费一个队列的消息,可以提高消息的并发处理速度:
接收消息(配置多个消费者)
通过@RabbitListener注解,配置concurrency参数即可实现。
如下,启动10个消费者并发处理消息:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.listener;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
// 声明消息监听器,通过queues参数指定监听的队列
// 关键参数:concurrency 代表当前监听器需要启动多少个消费者,类型是字符串
@RabbitListener(queues = "hello", concurrency = "10")
public class HelloListener {
// 使用RabbitHandler标记消息处理器,用来执行消息处理逻辑
@RabbitHandler
public void receive(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者 - 收到消息 '" + msg + "'");
}
}
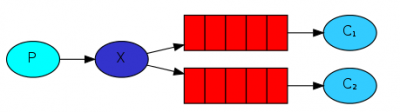
发布订阅模式
Java RabbitMQ发布订阅模式(广播模式、fanout模式),使用的交换机类型为FanoutExchange,就是一个生产者发送的消息会被多个队列的消费者处理:
发送消息
- 配置交换机:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class QueueConfig { // 定义交换机 @Bean public FanoutExchange fanout() { // 参数为交换机名字,不能重复 return new FanoutExchange("tizi365.fanout"); } }
- 发送消息:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.service; import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class SendService { @Autowired private RabbitTemplate template; @Autowired private FanoutExchange fanout; // 为演示,这里使用定时任务,每秒发送一条消息 @Scheduled(fixedDelay = 1000, initialDelay = 1000) public void send() { // 消息内容 String message = "Hello World!"; // 发送消息 // 第一个参数是交换机名字 // 第二个参数是路由参数,fanout交换机会忽略路由参数,所以不用设置 // 第三个参数是消息内容,支持任意类型,只要支持序列化 template.convertAndSend(fanout.getName(), "", message); System.out.println("发送消息 '" + message + "'"); } }
接收消息
- 配置交换机、队列及绑定:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class QueueConfig { // 定义交换机 @Bean public FanoutExchange fanout() { // 参数为交换机名字,不能重复 return new FanoutExchange("tizi365.fanout"); } @Bean public Queue queue1() { // 定义队列1 return new Queue("tizi365.fanout.queue1"); } @Bean public Queue queue2() { // 定义队列2 return new Queue("tizi365.fanout.queue2"); } @Bean public Binding binding1(FanoutExchange fanout, Queue queue1) { // 定义一个绑定关系,将队列1绑定到fanout交换机上 return BindingBuilder.bind(queue1).to(fanout); } @Bean public Binding binding2(FanoutExchange fanout, Queue queue2) { // 定义一个绑定关系,将队列2绑定到fanout交换机上 return BindingBuilder.bind(queue2).to(fanout); } }
- 接收消息:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.listener; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; // 将当前类交给Spring管理 @Component public class DemoListener { // 定义一个监听器,通过queues参数指定监听那个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "tizi365.fanout.queue1") public void receive1(String msg) { System.out.println("收到队列1的消息 = " + msg); } // 定义一个监听器,通过queues参数指定监听那个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "tizi365.fanout.queue2") public void receive2(String msg) { System.out.println("收到队列2的消息 = " + msg); } }
- 每一条消息,都会分发给所有绑定到当前交换机的队列中,消息会被上面的两个方法分别处理。
P.S. :全注解方式定义队列监听器
直接通过 @RabbitListener 注解的 bindings 参数定义绑定关系、队列、交换机:
- 不再需要消费者项目的配置类定义内容(交换机、队列和绑定关系);
@RabbitListener(
bindings = {
@QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "tizi365.fanout.queue3", durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "tizi365.fanout", durable = "true", type = ExchangeTypes.FANOUT)
)
}
)
public void receive3(String msg) {
System.out.println("收到队列3的消息 = " + msg);
}
说明:
- QueueBinding 注解:定义队列和交换机的绑定关系:“value”参数用于定义队列,“exchange”用于定义交换机;
- Queue 注解:定义一个队列:“name”参数定义队列名(需要唯一),“durable”参数表示是否需要持久化;
- Exchange 注解:定义一个交换机:“name”参数定义交换机的名字,“type”参数表示交换机的类型;
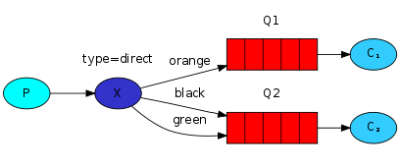
路由模式
Java RabbitMQ路由模式(Direct模式),使用的交换机类型为DirectExchange,跟发布订阅模式的区别就是 Direct 交换机将消息投递到路由参数完全匹配的队列中。
发送消息
- 配置交换机:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.*; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class QueueConfig { @Bean public DirectExchange direct() { // 定义交换机 // 参数为交换机名字,不能重复 return new DirectExchange("tizi365.direct"); } }
- 发送消息:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.service; import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class SendService { @Autowired private RabbitTemplate template; @Autowired private DirectExchange direct; // 为演示,这里使用定时任务,每秒发送一条消息 @Scheduled(fixedDelay = 1000, initialDelay = 1000) public void send() { // 消息内容 String message = "Hello World!"; // 发送消息 // 第一个参数是交换机名字 // 第二个参数是路由参数,direct交换机将消息投递到路由参数匹配tizi365的队列 // 第三个参数是消息内容,支持任意类型,只要支持序列化 template.convertAndSend(direct.getName(), "tizi365", message); System.out.println("发送消息 '" + message + "'"); } }
接收消息
- 配置交换机、队列及绑定:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.*; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class QueueConfig { @Bean public DirectExchange direct() { // 定义交换机 // 参数为交换机名字,不能重复 return new DirectExchange("tizi365.direct"); } @Bean public Queue queue1() { // 定义队列1 return new Queue("tizi365.direct.queue1"); } @Bean public Queue queue2() { // 定义队列2 return new Queue("tizi365.direct.queue2"); } @Bean public Binding binding1(DirectExchange direct, Queue queue1) { // 定义一个绑定关系,将队列1绑定到direct交换机上, 路由参数为:tizi365 // 路由参数匹配tizi365,交换机将消息投递到队列1 return BindingBuilder.bind(queue1).to(direct).with("tizi365"); } @Bean public Binding binding2(DirectExchange direct, Queue queue2) { // 定义一个绑定关系,将队列2绑定到direct交换机上, 路由参数为:baidu // 路由参数匹配baidu,交换机将消息投递到队列2 return BindingBuilder.bind(queue2).to(direct).with("baidu"); } }
- 接受消息:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.listener; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.*; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; // 将当前类交给Spring管理 @Component public class DemoListener { // 定义一个监听器,通过queues参数指定监听那个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "tizi365.direct.queue1") public void receive1(String msg) { System.out.println("收到队列1的消息 = " + msg); } // 定义一个监听器,通过queues参数指定监听那个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "tizi365.direct.queue2") public void receive2(String msg) { System.out.println("收到队列2的消息 = " + msg); } }
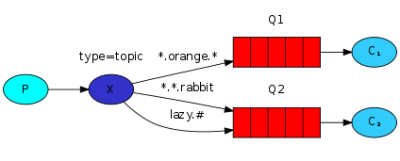
主题模式
Java RabbitMQ 主题模式(Topic模式),使用的交换机类型为TopicExchange,跟路由模式(Direct)的区别就路由参数支持模糊匹配。
- 因为路由匹配比较灵活,所以是比较常用的模式;
发送消息
- 配置交换机:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.*; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class QueueConfig { @Bean public TopicExchange topic() { // 定义交换机 // 参数为交换机名字,不能重复 return new TopicExchange("tizi365.topic"); } }
- 发送信息:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.service; import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange; import org.springframework.amqp.core.TopicExchange; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class SendService { @Autowired private RabbitTemplate template; @Autowired private TopicExchange topic; // 为演示,这里使用定时任务,每秒发送一条消息 @Scheduled(fixedDelay = 1000, initialDelay = 1000) public void send() { // 消息内容 String message = "Hello World!"; // 发送消息 // 第一个参数是交换机名字 // 第二个参数是路由参数,topic交换机将消息投递到路由参数匹配的队列 // 第三个参数是消息内容,支持任意类型,只要支持序列化 template.convertAndSend(topic.getName(), "www.tizi365.com", message); System.out.println("发送消息 '" + message + "'"); } }
接收消息
- 配置交换机、队列及绑定:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.config; import org.springframework.amqp.core.*; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration public class QueueConfig { @Bean public TopicExchange topic() { // 定义交换机 // 参数为交换机名字,不能重复 return new TopicExchange("tizi365.topic"); } @Bean public Queue queue1() { // 定义队列1 return new Queue("tizi365.topic.queue1"); } @Bean public Queue queue2() { // 定义队列2 return new Queue("tizi365.topic.queue2"); } @Bean public Binding binding1(TopicExchange topic, Queue queue1) { // 定义一个绑定关系,将队列1绑定到topic交换机上, 路由参数为:*.tizi365.com return BindingBuilder.bind(queue1).to(topic).with("*.tizi365.com"); } @Bean public Binding binding2(TopicExchange topic, Queue queue2) { // 定义一个绑定关系,将队列2绑定到direct交换机上, 路由参数为:*.baidu.com return BindingBuilder.bind(queue2).to(topic).with("*.baidu.com"); } }
- 支持的通配符:“#”匹配一个或多个单词;“*”:仅匹配一个单词。
- 接受消息:
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.listener; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.*; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; // 将当前类交给Spring管理 @Component public class DemoListener { // 定义一个监听器,通过queues参数指定监听那个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "tizi365.topic.queue1") public void receive1(String msg) { System.out.println("收到队列1的消息 = " + msg); } // 定义一个监听器,通过queues参数指定监听那个队列 @RabbitListener(queues = "tizi365.topic.queue2") public void receive2(String msg) { System.out.println("收到队列2的消息 = " + msg); } }
使用自定义消息类型
前面我们发送的消息是一个字符串类型,实际业务中我们更愿意直接发送各种自定义Java对象类型的数据。
定义一个实体对象
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
import lombok.Data;
// 博客内容
@Data
public class Blog implements Serializable {
// id
private Integer id;
// 标题
private String title;
}
发送自定义类型消息
Blog blog = new Blog();
blog.setId(100);
blog.setTitle("Tizi365 RabbitMQ教程");
// 发送消息
template.convertAndSend(helloQueue.getName(), blog);
接收自定义类型消息
@RabbitHandler
// 方法参数改为自定义消息类型即可
public void receive(Blog msg) {
System.out.println("消费者 - 收到消息 '" + msg.getTitle() + "'");
}
使用Json序列化消息内容
RabbitMQ 发送Java实体对象数据的时候,默认使用JDK的对象序列化工具。我们可以改成使用json格式对数据进行序列化,这样可以支持其他类型的语言消费Java发送出去的消息,同时也让消息格式更具有可读性。
修改以前的配置类,增加下面配置, 使用Jackson json解析器对消息数据进行序列化和反序列化。
@Bean
public Jackson2JsonMessageConverter messageConverter() {
// 设置默认消息转换器
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}