“RabbitMQ:SpringBoot集成”的版本间差异
跳到导航
跳到搜索
(→死信队列实现) |
|||
| 第1,322行: | 第1,322行: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
==== 场景二:消息过期 ==== | |||
消息过期,过了TTL存活时间。 | 消息过期,过了TTL存活时间。 | ||
2021年5月27日 (四) 20:39的版本
SpringBoot 集成 RabbitMQ
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
RabbitMQ 配置
(application.yml中)
简单配置:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 127.0.0.1 #ip
port: 5672 #端口
username: guest #账号
password: guest #密码
P.S.:全量配置说明
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 127.0.0.1 #ip
port: 5672 #端口
username: guest #账号
password: guest #密码
virtualHost: #链接的虚拟主机
addresses: 127.0.0.1:5672 #多个以逗号分隔,与host功能一样。
requestedHeartbeat: 60 #指定心跳超时,单位秒,0为不指定;默认60s
publisherConfirms: true #发布确认机制是否启用
publisherReturns: #发布返回是否启用
connectionTimeout: #链接超时。单位ms。0表示无穷大不超时
### ssl相关
ssl:
enabled: #是否支持ssl
keyStore: #指定持有SSL certificate的key store的路径
keyStoreType: #key store类型 默认PKCS12
keyStorePassword: #指定访问key store的密码
trustStore: #指定持有SSL certificates的Trust store
trustStoreType: #默认JKS
trustStorePassword: #访问密码
algorithm: #ssl使用的算法,例如,TLSv1.1
verifyHostname: #是否开启hostname验证
### cache相关
cache:
channel:
size: #缓存中保持的channel数量
checkoutTimeout: #当缓存数量被设置时,从缓存中获取一个channel的超时时间,单位毫秒;如果为0,则总是创建一个新channel
connection:
mode: #连接工厂缓存模式:CHANNEL 和 CONNECTION
size: #缓存的连接数,只有是CONNECTION模式时生效
### listener
listener:
type: #两种类型,SIMPLE,DIRECT
## simple类型
simple:
concurrency: #最小消费者数量
maxConcurrency: #最大的消费者数量
transactionSize: #指定一个事务处理的消息数量,最好是小于等于prefetch的数量
missingQueuesFatal: #是否停止容器当容器中的队列不可用
## 与direct相同配置部分
autoStartup: #是否自动启动容器
acknowledgeMode: #表示消息确认方式,其有三种配置方式,分别是none、manual和auto;默认auto
prefetch: #指定一个请求能处理多少个消息,如果有事务的话,必须大于等于transaction数量
defaultRequeueRejected: #决定被拒绝的消息是否重新入队;默认是true(与参数acknowledge-mode有关系)
idleEventInterval: #container events发布频率,单位ms
##重试机制
retry:
stateless: #有无状态
enabled: #是否开启
maxAttempts: #最大重试次数,默认3
initialInterval: #重试间隔
multiplier: #对于上一次重试的乘数
maxInterval: #最大重试时间间隔
direct:
consumersPerQueue: #每个队列消费者数量
missingQueuesFatal:
#...其余配置看上方公共配置
## template相关
template:
mandatory: #是否启用强制信息;默认false
receiveTimeout: #`receive()`接收方法超时时间
replyTimeout: #`sendAndReceive()`超时时间
exchange: #默认的交换机
routingKey: #默认的路由
defaultReceiveQueue: #默认的接收队列
## retry重试相关
retry:
enabled: #是否开启
maxAttempts: #最大重试次数
initialInterval: #重试间隔
multiplier: #失败间隔乘数
maxInterval: #最大间隔
关键代码
配置类:
@Bean
public AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate() {
Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RabbitTemplate.class);
// 使用jackson 消息转换器
rabbitTemplate.setMessageConverter(new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter());
rabbitTemplate.setEncoding("UTF-8");
// 消息发送失败返回到队列中,yml需要配置 publisher-returns: true
rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true);
rabbitTemplate.setReturnCallback((message, replyCode, replyText, exchange, routingKey) -> {
String correlationId = message.getMessageProperties().getCorrelationIdString();
log.debug("消息:{} 发送失败, 应答码:{} 原因:{} 交换机: {} 路由键: {}", correlationId, replyCode, replyText, exchange, routingKey);
});
// 消息确认,yml需要配置 publisher-confirms: true
rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback((correlationData, ack, cause) -> {
if (ack) {
log.debug("消息发送到exchange成功,id: {}", correlationData.getId());
} else {
log.debug("消息发送到exchange失败,原因: {}", cause);
}
});
return rabbitTemplate;
}
/**
* 声明Direct交换机 支持持久化.
*
* @return the exchange
*/
@Bean("directExchange")
public Exchange directExchange() {
return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange("DIRECT_EXCHANGE").durable(true).build();
}
/**
* 声明一个队列 支持持久化.
*
* @return the queue
*/
@Bean("directQueue")
public Queue directQueue() {
return QueueBuilder.durable("DIRECT_QUEUE").build();
}
/**
* 通过绑定键 将指定队列绑定到一个指定的交换机 .
*
* @param queue the queue
* @param exchange the exchange
* @return the binding
*/
@Bean
public Binding directBinding(@Qualifier("directQueue") Queue queue,
@Qualifier("directExchange") Exchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("DIRECT_ROUTING_KEY").noargs();
}
生产者:
// 发送消息
rabbitTemplate.setExchange(exchange);
rabbitTemplate.setRoutingKey(routeKey);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(message);
// 发送消息
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, routeKey, message);
// 发送消息:为消息设置关联数据???
CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, routeKey, message, correlationData);
// 发送消息:为消息设置过期时间
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend(exchange, routeKey, message,
new MessagePostProcessor() {
@Override
public Message postProcessMessage(Message message) throws AmqpException {
//给消息设置延迟毫秒值
message.getMessageProperties().setExpiration(String.valueOf(delayTimes));
return message;
}
});
消费者:
// 基础注解,指定queue的名称,可以多个。除 simple/Work 模式外,都需要配置类来配置queue、exchange及他绑定关系
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue")
@RabbitHandler
public void processSimpleMsg(String message) {
System.out.println("########################received simple" + message);
}
// 如果不想使用配置类,可以直接注解通过 bindings,绑定,spring 会根据注解生成绑定
// ps:如果已有同名称的类。不会覆盖。会影响功能
@RabbitListener(bindings = { @QueueBinding( value = @Queue(value = "queue", durable = "true"),
exchange = @Exchange(value = "exchange", type = "direct"),
key = {"routeKey1","routeKey2"})
})
@RabbitHandler
public void processDirectMsg(String message) {
System.out.println("########################received" + message);
}
常用注解说明
@Exchange
@Exchange 是声明交换及交换机的一些属性:
@Target({})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Exchange {
String TRUE = "true";
String FALSE = "false";
/**
* @return the exchange name.
*/
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
/**
* @return the exchange name.
* @since 2.0
*/
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
/**
* 交换机类型,默认DIRECT
*/
String type() default ExchangeTypes.DIRECT;
/**
* 是否持久化
*/
String durable() default TRUE;
/**
* 是否自动删除
*/
String autoDelete() default FALSE;
/**
* @return the arguments to apply when declaring this exchange.
* @since 1.6
*/
Argument[] arguments() default {};
}
@Queue
@Queue 是声明队列及队列的一些属性,主要参数如下:
@Target({})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Queue {
/**
* @return the queue name or "" for a generated queue name (default).
*/
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
/**
* @return the queue name or "" for a generated queue name (default).
* @since 2.0
*/
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
/**
* 是否持久化
*/
String durable() default "";
/**
* 是否独享、排外的.
*/
String exclusive() default "";
/**
* 是否自动删除;
*/
String autoDelete() default "";
/**
* 队列的其他属性参数
*(1)x-message-ttl:消息的过期时间,单位:毫秒;
*(2)x-expires:队列过期时间,队列在多长时间未被访问将被删除,单位:毫秒;
*(3)x-max-length:队列最大长度,超过该最大值,则将从队列头部开始删除消息;
*(4)x-max-length-bytes:队列消息内容占用最大空间,受限于内存大小,超过该阈值则从队列头部开始删除消息;
*(5)x-overflow:设置队列溢出行为。这决定了当达到队列的最大长度时消息会发生什么。有效值是drop-head、reject-publish或reject-publish-dlx。仲裁队列类型仅支持drop-head;
*(6)x-dead-letter-exchange:死信交换器名称,过期或被删除(因队列长度超长或因空间超出阈值)的消息可指定发送到该交换器中;
*(7)x-dead-letter-routing-key:死信消息路由键,在消息发送到死信交换器时会使用该路由键,如果不设置,则使用消息的原来的路由键值
*(8)x-single-active-consumer:表示队列是否是单一活动消费者,true时,注册的消费组内只有一个消费者消费消息,其他被忽略,false时消息循环分发给所有消费者(默认false)
*(9)x-max-priority:队列要支持的最大优先级数;如果未设置,队列将不支持消息优先级;
*(10)x-queue-mode(Lazy mode):将队列设置为延迟模式,在磁盘上保留尽可能多的消息,以减少RAM的使用;如果未设置,队列将保留内存缓存以尽可能快地传递消息;
*(11)x-queue-master-locator:在集群模式下设置镜像队列的主节点信息。
*/
Argument[] arguments() default {};
}
@QueueBinding
@QueueBinding作用就是将队列和交换机进行绑定,主要有以下三个参数:
@Target({})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface QueueBinding {
/**
* @return the queue.
*/
Queue value();
/**
* @return the exchange.
*/
Exchange exchange();
/**
* @return the routing key or pattern for the binding.
* Multiple elements will result in multiple bindings.
*/
String[] key() default {};
}
集成示例
- maven:
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.9.6</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>com.vaadin.external.google</groupId> <artifactId>android-json</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> </dependencies>
- application.yml:
spring: rabbitmq: host: 127.0.0.1 port: 5672 username: spring password: 123456 publisher-confirms: true #支持发布确认 publisher-returns: true #支持发布返回 listener: simple: acknowledge-mode: manual #采用手动应答 concurrency: 1 #指定最小的消费者数量 max-concurrency: 1 #指定最大的消费者数量 retry: enabled: true #是否支持重试
- 配置类:
- 定制模版类、声明交换机、队列、绑定交换机到队列;
@Configuration public class RabbitConfig { @Resource private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; /** * 定制化amqp模版 可根据需要定制多个 * <p> * <p> * 此处为模版类定义 Jackson 消息转换器 * ConfirmCallback 接口用于实现消息发送到 RabbitMQ 交换器后接收 ack 回调 即消息发送到exchange ack * ReturnCallback 接口用于实现消息发送到 RabbitMQ 交换器,但无相应队列与交换器绑定时的回调 即消息发送不到任何一个队列中 ack * * @return the amqp template */ // @Primary @Bean public AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate() { Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RabbitTemplate.class); // 使用jackson 消息转换器 rabbitTemplate.setMessageConverter(new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter()); rabbitTemplate.setEncoding("UTF-8"); // 消息发送失败返回到队列中,yml需要配置 publisher-returns: true rabbitTemplate.setMandatory(true); rabbitTemplate.setReturnCallback((message, replyCode, replyText, exchange, routingKey) -> { String correlationId = message.getMessageProperties().getCorrelationIdString(); log.debug("消息:{} 发送失败, 应答码:{} 原因:{} 交换机: {} 路由键: {}", correlationId, replyCode, replyText, exchange, routingKey); }); // 消息确认,yml需要配置 publisher-confirms: true rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback((correlationData, ack, cause) -> { if (ack) { log.debug("消息发送到exchange成功,id: {}", correlationData.getId()); } else { log.debug("消息发送到exchange失败,原因: {}", cause); } }); return rabbitTemplate; } /* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------Direct exchange test--------------------------------------------------------------------------- */ /** * 声明Direct交换机 支持持久化. * * @return the exchange */ @Bean("directExchange") public Exchange directExchange() { return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange("DIRECT_EXCHANGE").durable(true).build(); } /** * 声明一个队列 支持持久化. * * @return the queue */ @Bean("directQueue") public Queue directQueue() { return QueueBuilder.durable("DIRECT_QUEUE").build(); } /** * 通过绑定键 将指定队列绑定到一个指定的交换机 . * * @param queue the queue * @param exchange the exchange * @return the binding */ @Bean public Binding directBinding(@Qualifier("directQueue") Queue queue, @Qualifier("directExchange") Exchange exchange) { return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(exchange).with("DIRECT_ROUTING_KEY").noargs(); } /* ----------------------------------------------------------------------------Fanout exchange test--------------------------------------------------------------------------- */ /** * 声明 fanout 交换机. * * @return the exchange */ @Bean("fanoutExchange") public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange() { return (FanoutExchange) ExchangeBuilder.fanoutExchange("FANOUT_EXCHANGE").durable(true).build(); } /** * Fanout queue A. * * @return the queue */ @Bean("fanoutQueueA") public Queue fanoutQueueA() { return QueueBuilder.durable("FANOUT_QUEUE_A").build(); } /** * Fanout queue B . * * @return the queue */ @Bean("fanoutQueueB") public Queue fanoutQueueB() { return QueueBuilder.durable("FANOUT_QUEUE_B").build(); } /** * 绑定队列A 到Fanout 交换机. * * @param queue the queue * @param fanoutExchange the fanout exchange * @return the binding */ @Bean public Binding bindingA(@Qualifier("fanoutQueueA") Queue queue, @Qualifier("fanoutExchange") FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) { return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(fanoutExchange); } /** * 绑定队列B 到Fanout 交换机. * * @param queue the queue * @param fanoutExchange the fanout exchange * @return the binding */ @Bean public Binding bindingB(@Qualifier("fanoutQueueB") Queue queue, @Qualifier("fanoutExchange") FanoutExchange fanoutExchange) { return BindingBuilder.bind(queue).to(fanoutExchange); } }
- 生产者:
@Service public class SenderService { private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass()); @Resource private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; /** * 测试广播模式. * * @param p the p * @return the response entity */ public void broadcast(String p) { CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData(UUID.randomUUID().toString()); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("FANOUT_EXCHANGE", "", p, correlationData); } /** * 测试Direct模式. * * @param p the p * @return the response entity */ public void direct(String p) { CorrelationData correlationData = new CorrelationData(UUID.randomUUID().toString()); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("DIRECT_EXCHANGE", "DIRECT_ROUTING_KEY", p, correlationData); } }
- 消费者:
@Component public class Receiver { private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Receiver.class); /** * FANOUT广播队列监听一. * * @param message the message * @param channel the channel * @throws IOException the io exception 这里异常需要处理 */ @RabbitListener(queues = {"FANOUT_QUEUE_A"}) public void on(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException { channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), true); log.debug("FANOUT_QUEUE_A " + new String(message.getBody())); } /** * FANOUT广播队列监听二. * * @param message the message * @param channel the channel * @throws IOException the io exception 这里异常需要处理 */ @RabbitListener(queues = {"FANOUT_QUEUE_B"}) public void t(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException { channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), true); log.debug("FANOUT_QUEUE_B " + new String(message.getBody())); } /** * DIRECT模式. * * @param message the message * @param channel the channel * @throws IOException the io exception 这里异常需要处理 */ @RabbitListener(queues = {"DIRECT_QUEUE"}) public void message(Message message, Channel channel) throws IOException { channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), true); log.debug("DIRECT " + new String(message.getBody())); } }
使用自定义消息类型
前面我们发送的消息是一个字符串类型,实际业务中我们更愿意直接发送各种自定义Java对象类型的数据。
定义一个实体对象
package com.tizi365.rabbitmq.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
import lombok.Data;
// 博客内容
@Data
public class Blog implements Serializable {
// id
private Integer id;
// 标题
private String title;
}
发送自定义类型消息
Blog blog = new Blog();
blog.setId(100);
blog.setTitle("Tizi365 RabbitMQ教程");
// 发送消息
template.convertAndSend(helloQueue.getName(), blog);
接收自定义类型消息
@RabbitHandler
// 方法参数改为自定义消息类型即可
public void receive(Blog msg) {
System.out.println("消费者 - 收到消息 '" + msg.getTitle() + "'");
}
使用Json序列化消息内容
RabbitMQ 发送Java实体对象数据的时候,默认使用JDK的对象序列化工具。我们可以改成使用json格式对数据进行序列化,这样可以支持其他类型的语言消费Java发送出去的消息,同时也让消息格式更具有可读性。
修改以前的配置类,增加下面配置, 使用Jackson json解析器对消息数据进行序列化和反序列化。
@Bean
public Jackson2JsonMessageConverter messageConverter() {
// 设置默认消息转换器
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}
延迟消息实现(死信队列 + 消息TTL)
场景:
- 用于解决用户下单以后,订单超时如何取消订单的问题:
- - 用户进行提交订单操作(会有锁定商品库存等操作);
- - 生成订单,获取订单的id;
- - 获取到设置的订单超时时间(假设设置的为60分钟不支付取消订单);
- - 按订单超时时间发送一个延迟消息给 RabbitMQ,让它在订单超时后触发取消订单的操作;
- - 如果用户没有支付,进行取消订单操作(释放锁定商品库存一系列操作)。
- 实现方法:需要一个订单延迟消息队列,以及一个取消订单消息队列:一旦有消息以延迟订单设置的路由键发送过来,会转发到订单延迟消息队列,并在此队列保存一定时间,等到超时后会自动将消息发送到取消订单消息消费队列。
- 短信验证码以及邮箱验证码都采用消息队列进行消费:
- 采用队列,交换机,路由键进行消费。一条队列,一个交换机,一个路由键就可以实现。
实现
- pom.xml:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId> </dependency>
- application.yml:
# SpringBoot配置RabbitMq rabbitmq: host: localhost # rabbitmq的连接地址 port: 5672 # rabbitmq的连接端口号 virtual-host: /hanzoMall # rabbitmq的虚拟host username: hanzoMall # rabbitmq的用户名 password: hanzoMall # rabbitmq的密码 publisher-confirms: true #如果对异步消息需要回调必须设置为true
- 消息队列枚举配置:
package ltd.hanzo.mall.common; import com.rabbitmq.client.AMQP; import lombok.Getter; @Getter public enum QueueEnum { /** * 短信消息通知队列 * exchange:mall.sms.direct * queue:mall.sms.send * routeKey:mall.sms.send */ QUEUE_SMS_SEND("mall.sms.direct", "mall.sms.send", "mall.sms.send"), /** * 邮件消息通知队列 * exchange:mall.email.direct * queue:mall.email.send * routeKey:mall.email.send */ QUEUE_EMAIL_SEND("mall.email.direct", "mall.email.send", "mall.email.send"), /** * “订单取消”消息通知队列 * exchange:mall.order.direct * queue:mall.order.cancel * routeKey:mall.order.cancel */ QUEUE_ORDER_CANCEL("mall.order.direct", "mall.order.cancel", "mall.order.cancel"), /** * “订单延迟”消息通知队列 * exchange:mall.order.direct.ttl * queue:mall.order.cancel.ttl * routeKey:mall.order.cancel.ttl * 订单消息会被转发到此队列,并在此队列保存一定时间,等到超时后会自动将消息发送到 mall.order.cancel(取消订单消息消费队列)。 */ QUEUE_TTL_ORDER_CANCEL("mall.order.direct.ttl", "mall.order.cancel.ttl", "mall.order.cancel.ttl"); /** * 交换机名称 */ private String exchange; /** * 队列名称 */ private String name; /** * 路由键 */ private String routeKey; QueueEnum(String exchange, String name, String routeKey) { this.exchange = exchange; this.name = name; this.routeKey = routeKey; } }
- RabbitMQ 配置类:
package ltd.hanzo.mall.config; import ltd.hanzo.mall.common.QueueEnum; import org.springframework.amqp.core.*; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; */ @Configuration public class RabbitMqConfig { /* --------------------------------------------------------1、短信消息队列------------------------------------------------------- */ /** * 交换机 */ @Bean DirectExchange sendSmsDirect() { return (DirectExchange) ExchangeBuilder .directExchange(QueueEnum.QUEUE_SMS_SEND.getExchange()) .durable(true) .build(); } /** * 队列 */ @Bean public Queue sendSmsQueue() { return new Queue(QueueEnum.QUEUE_SMS_SEND.getName()); } /** * 绑定 */ @Bean Binding sendSmsBinding(DirectExchange sendSmsDirect, Queue sendSmsQueue){ return BindingBuilder .bind(sendSmsQueue) .to(sendSmsDirect) .with(QueueEnum.QUEUE_SMS_SEND.getRouteKey()); } /* --------------------------------------------------------2、邮件消息队列------------------------------------------------------- */ /** * 交换机 */ @Bean DirectExchange sendEmailDirect() { return (DirectExchange) ExchangeBuilder .directExchange(QueueEnum.QUEUE_EMAIL_SEND.getExchange()) .durable(true) .build(); } /** * 队列 */ @Bean public Queue sendEmailQueue() { return new Queue(QueueEnum.QUEUE_EMAIL_SEND.getName()); } /** * 绑定 */ @Bean Binding sendEmailBinding(DirectExchange sendEmailDirect, Queue sendEmailQueue){ return BindingBuilder .bind(sendEmailQueue) .to(sendEmailDirect) .with(QueueEnum.QUEUE_EMAIL_SEND.getRouteKey()); } /* --------------------------------------------------------3、订单取消队列------------------------------------------------------- */ /** * 交换机 */ @Bean DirectExchange orderDirect() { return (DirectExchange) ExchangeBuilder .directExchange(QueueEnum.QUEUE_ORDER_CANCEL.getExchange()) .durable(true) .build(); } /** * 队列 */ @Bean public Queue orderQueue() { return new Queue(QueueEnum.QUEUE_ORDER_CANCEL.getName()); } /** * 绑定 */ @Bean Binding orderBinding(DirectExchange orderDirect,Queue orderQueue){ return BindingBuilder .bind(orderQueue) .to(orderDirect) .with(QueueEnum.QUEUE_ORDER_CANCEL.getRouteKey()); } /* --------------------------------------------------------4、订单延迟队列------------------------------------------------------- */ /** * 交换机 */ @Bean DirectExchange orderTtlDirect() { return (DirectExchange) ExchangeBuilder .directExchange(QueueEnum.QUEUE_TTL_ORDER_CANCEL.getExchange()) .durable(true) .build(); } /** * 队列(死信队列) */ @Bean public Queue orderTtlQueue() { return QueueBuilder .durable(QueueEnum.QUEUE_TTL_ORDER_CANCEL.getName()) .withArgument("x-dead-letter-exchange", QueueEnum.QUEUE_ORDER_CANCEL.getExchange()) // 到期后转发的交换机 .withArgument("x-dead-letter-routing-key", QueueEnum.QUEUE_ORDER_CANCEL.getRouteKey()) // 到期后转发的路由键 .build(); } /** * 绑定 */ @Bean Binding orderTtlBinding(DirectExchange orderTtlDirect,Queue orderTtlQueue){ return BindingBuilder .bind(orderTtlQueue) .to(orderTtlDirect) .with(QueueEnum.QUEUE_TTL_ORDER_CANCEL.getRouteKey()); } }
- “订单延迟”发送者:向订单延迟消息队列(mall.order.cancel.ttl)里发送消息
package ltd.hanzo.mall.component; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import ltd.hanzo.mall.common.QueueEnum; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.amqp.AmqpException; import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate; import org.springframework.amqp.core.Message; import org.springframework.amqp.core.MessagePostProcessor; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @Slf4j public class CancelOrderSender { @Autowired private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate; public void sendMessage(String orderNo,final long delayTimes){ // 给延迟队列发送消息 amqpTemplate.convertAndSend(QueueEnum.QUEUE_TTL_ORDER_CANCEL.getExchange(), QueueEnum.QUEUE_TTL_ORDER_CANCEL.getRouteKey(), orderNo, new MessagePostProcessor() { @Override public Message postProcessMessage(Message message) throws AmqpException { // 给消息设置延迟毫秒值 message.getMessageProperties().setExpiration(String.valueOf(delayTimes)); return message; } }); log.info("send delay message orderNo:{}",orderNo); } }
- “订单延迟”队列(mall.order.cancel.ttl)中消息过期之后就会被转发到达“订单取消”队列(mall.order.cancel);
- “订单取消”接收者:用于从取消订单的消息队列(mall.order.cancel)里接收消息
package ltd.hanzo.mall.component; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import ltd.hanzo.mall.service.HanZoMallOrderService; import ltd.hanzo.mall.service.TaskService; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler; import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component @RabbitListener(queues = "mall.order.cancel") @Slf4j public class CancelOrderReceiver { @Autowired private HanZoMallOrderService hanZoMallOrderService; @Autowired private TaskService taskService; @RabbitHandler public void handle(String orderNo){ log.info("receive delay message orderNo:{}",orderNo); hanZoMallOrderService.cancelOrder(orderNo); taskService.cancelOrderSendSimpleMail(orderNo); } }
- HanZoMallOrderService接口:创建订单,取消超时订单
public interface HanZoMallOrderService { /** * 保存订单 * * @param user * @param myShoppingCartItems * @return */ String saveOrder(HanZoMallUserVO user, List<HanZoMallShoppingCartItemVO> myShoppingCartItems); /** * 取消单个超时订单 */ @Transactional void cancelOrder(String orderNo); }
- HanZoMallOrderServiceImpl实现类:实现 HanZoMallOrderService 接口
@Slf4j @Service public class HanZoMallOrderServiceImpl implements HanZoMallOrderService { @Resource private HanZoMallOrderMapper hanZoMallOrderMapper; @Resource private HanZoMallOrderItemMapper hanZoMallOrderItemMapper; @Resource private HanZoMallShoppingCartItemMapper hanZoMallShoppingCartItemMapper; @Resource private HanZoMallGoodsMapper hanZoMallGoodsMapper; @Autowired private CancelOrderSender cancelOrderSender; @Override @Transactional public String saveOrder(HanZoMallUserVO user, List<HanZoMallShoppingCartItemVO> myShoppingCartItems) { // todo 执行一系类下单操作,代码在github中 // 下单完成后开启一个延迟消息,用于当用户没有付款时取消订单 sendDelayMessageCancelOrder(orderNo); // 所有操作成功后,将订单号返回,以供Controller方法跳转到订单详情 return orderNo; } @Override public void cancelOrder(String orderNo) { HanZoMallOrder hanZoMallOrder = hanZoMallOrderMapper.selectByOrderNo(orderNo); if (hanZoMallOrder != null && hanZoMallOrder.getOrderStatus() == 0) { // 超时取消订单 hanZoMallOrderMapper.closeOrder(Collections.singletonList(hanZoMallOrder.getOrderId()), HanZoMallOrderStatusEnum.ORDER_CLOSED_BY_EXPIRED.getOrderStatus()); } } private void sendDelayMessageCancelOrder(String orderNo) { // 获取订单超时时间,假设为60分钟 long delayTimes = 36 * 100000; // 发送延迟消息 cancelOrderSender.sendMessage(orderNo, delayTimes); } }
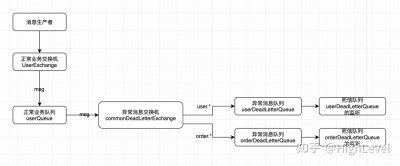
死信队列实现
死信队列可以实现消息在未被正常消费的场景下,对这些消息进行其他处理,保证消息不会被丢弃。
死信场景:
- 消息被消费者拒绝签收,并且重新入队为false:(basic.reject() / basic.nack())and requeue = false。
- 注意:消费者设置了自动 ACK,当重复投递次数达到了设置的最大 retry 次数之后,消息也会投递到死信队列,但是内部的原理还是调用了 nack/reject。
- 消息过期,过了 TTL 存活时间。
- 队列设置了 x-max-length 最大消息数量且当前队列中的消息已经达到了这个数量,再次投递,消息将被挤掉,被挤掉的是最靠近被消费那一端的消息。
实现
- 正常业务消息被投递到正常业务的Exchange,该Exchange根据路由键将消息路由到绑定的正常队列。
- 正常业务队列中的消息变成了死信消息之后,会被自动投递到该队列绑定的死信交换机上(并带上配置的路由键,如果没有指定死信消息的路由键,则默认继承该消息在正常业务时设定的路由键)。
- 死信交换机收到消息后,将消息根据路由规则路由到指定的死信队列。
- 消息到达死信队列后,可监听该死信队列,处理死信消息。
- application.yml:
spring: application: name: learn-rabbitmq rabbitmq: host: localhost port: 5672 username: futao password: 123456789 virtual-host: deadletter-vh connection-timeout: 15000 # 发送确认 publisher-confirms: true # 路由失败回调 publisher-returns: true template: # 必须设置成true 消息路由失败通知监听者,而不是将消息丢弃 mandatory: true listener: simple: # 每次从RabbitMQ获取的消息数量 prefetch: 1 default-requeue-rejected: false # 每个队列启动的消费者数量 concurrency: 1 # 每个队列最大的消费者数量 max-concurrency: 1 # 签收模式为手动签收-那么需要在代码中手动ACK acknowledge-mode: manual app: rabbitmq: # 队列定义 queue: # 正常业务队列 user: user-queue # 死信队列 user-dead-letter: user-dead-letter-queue # 交换机定义 exchange: # 正常业务交换机 user: user-exchange # 死信交换机 common-dead-letter: common-dead-letter-exchange
- RabbitMQ 配置类:
@Configuration public class Declare { /* --------------------------------------------------------1、用户消息队列------------------------------------------------------- */ /** * 用户交换机 * * @param userExchangeName 用户交换机名 * @return */ @Bean public Exchange userExchange(@Value("${app.rabbitmq.exchange.user}") String userExchangeName) { return ExchangeBuilder .topicExchange(userExchangeName) .durable(true) .build(); } /** * 用户队列 * * @param userQueueName 用户队列名 * @return */ @Bean public Queue userQueue(@Value("${app.rabbitmq.queue.user}") String userQueueName, @Value("${app.rabbitmq.exchange.common-dead-letter}") String commonDeadLetterExchange) { return QueueBuilder .durable(userQueueName) //声明该队列的死信消息发送到的 交换机 (队列添加了这个参数之后会自动与该交换机绑定,并设置路由键,不需要开发者手动设置) .withArgument("x-dead-letter-exchange", commonDeadLetterExchange) //声明该队列死信消息在交换机的 路由键 .withArgument("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "user-dead-letter-routing-key") .build(); } /** * 用户队列与交换机绑定 * * @param userQueue 用户队列名 * @param userExchange 用户交换机名 * @return */ @Bean public Binding userBinding(Queue userQueue, Exchange userExchange) { return BindingBuilder .bind(userQueue) .to(userExchange) .with("user.*") .noargs(); } /* --------------------------------------------------------2、死信消息队列------------------------------------------------------- */ /** * 死信交换机 * * @param commonDeadLetterExchange 通用死信交换机名 * @return */ @Bean public Exchange commonDeadLetterExchange(@Value("${app.rabbitmq.exchange.common-dead-letter}") String commonDeadLetterExchange) { return ExchangeBuilder .topicExchange(commonDeadLetterExchange) .durable(true) .build(); } /** * 死信交换机 * * 用这个队列来接收 user-queue 的死信消息 * 用户队列 user-queue 的死信投递到死信交换机`common-dead-letter-exchange`后再投递到该队列 * @return */ @Bean public Queue userDeadLetterQueue(@Value("${app.rabbitmq.queue.user-dead-letter}") String userDeadLetterQueue) { return QueueBuilder .durable(userDeadLetterQueue) .build(); } /** * 死信队列绑定死信交换机 * * @param userDeadLetterQueue user-queue对应的死信队列 * @param commonDeadLetterExchange 通用死信交换机 * @return */ @Bean public Binding userDeadLetterBinding(Queue userDeadLetterQueue, Exchange commonDeadLetterExchange) { return BindingBuilder .bind(userDeadLetterQueue) .to(commonDeadLetterExchange) .with("user-dead-letter-routing-key") .noargs(); } }
- 生产者:
@Component public class DeadLetterSender { @Autowired private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate; @Value("${app.rabbitmq.exchange.user}") private String userExchange; public void send() { User user = User.builder() .userName("天文") .address("浙江杭州") .birthday(LocalDate.now(ZoneOffset.ofHours(8))) .build(); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(userExchange, "user.abc", user); } }
场景一:(basic.reject() / basic.nack())and requeue = false
消息被(basic.reject() or basic.nack()) and requeue = false,即消息被消费者拒绝或者nack,并且重新入队为false。
- nack()支持批量确认,而reject()不支持。
- 消费者:
@Slf4j @Component public class Consumer { /** * 正常用户队列消息监听消费者 * * @param user * @param message * @param channel */ @RabbitListener(queues = "${app.rabbitmq.queue.user}") public void userConsumer(User user, Message message, Channel channel) { log.info("正常用户业务监听:接收到消息:[{}]", JSON.toJSONString(user)); try { //参数为:消息的DeliveryTag,是否批量拒绝,是否重新入队 channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false, false); log.info("拒绝签收...消息的路由键为:[{}]", message.getMessageProperties().getReceivedRoutingKey()); } catch (IOException e) { log.error("消息拒绝签收失败", e); } } /** * @param user * @param message * @param channel */ @RabbitListener(queues = "${app.rabbitmq.queue.user-dead-letter}") public void userDeadLetterConsumer(User user, Message message, Channel channel) { log.info("接收到死信消息:[{}]", JSON.toJSONString(user)); try { channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false); log.info("死信队列签收消息....消息路由键为:[{}]", message.getMessageProperties().getReceivedRoutingKey()); } catch (IOException e) { log.error("死信队列消息签收失败", e); } } }
(autoACK and 重复投递次数>retry)
- application.yml:
spring: application: name: learn-rabbitmq rabbitmq: . . . listener: simple: # 每次从RabbitMQ获取的消息数量 prefetch: 1 default-requeue-rejected: false # 每个队列启动的消费者数量 concurrency: 1 # 每个队列最大的消费者数量 max-concurrency: 1 # 自动签收 acknowledge-mode: auto retry: enabled: true # 第一次尝试时间间隔 initial-interval: 10S # 两次尝试之间的最长持续时间。 max-interval: 10S # 最大重试次数(=第一次正常投递1+重试次数4) max-attempts: 5 # 上一次重试时间的乘数 multiplier: 1.0 . . .
- 消费者:
@Slf4j @Configuration public class AutoAckConsumer { /** * 正常用户队列消息监听消费者 * * @param user */ @RabbitListener(queues = "${app.rabbitmq.queue.user}") public void userConsumer(User user) { log.info("正常用户业务监听:接收到消息:[{}]", JSON.toJSONString(user)); throw new RuntimeException("模拟发生异常"); } /** * @param user */ @RabbitListener(queues = "${app.rabbitmq.queue.user-dead-letter}") public void userDeadLetterConsumer(User user) { log.info("接收到死信消息并自动签收:[{}]", JSON.toJSONString(user)); } }
场景二:消息过期
消息过期,过了TTL存活时间。
- RabbitMQ 配置类:设置队列消息的过期时间 x-message-ttl;
. . . /** * 用户队列 * * @param userQueueName 用户队列名 * @return */ @Bean public Queue userQueue(@Value("${app.rabbitmq.queue.user}") String userQueueName, @Value("${app.rabbitmq.exchange.common-dead-letter}") String commonDeadLetterExchange) { return QueueBuilder .durable(userQueueName) // 声明该队列的死信消息发送到的 交换机 (队列添加了这个参数之后会自动与该交换机绑定,并设置路由键,不需要开发者手动设置) .withArgument("x-dead-letter-exchange", commonDeadLetterExchange) // 声明该队列死信消息在交换机的 路由键 .withArgument("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "user-dead-letter-routing-key") // 该队列的消息的过期时间-超过这个时间还未被消费则路由到死信队列 .withArgument("x-message-ttl", 5000) .build(); } . . .
- 生产者:为每条消息设定过期时间
. . . log.info("消息投递...指定的存活时长为:[{}]ms", exp); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(userExchange, "user.abc", user, new MessagePostProcessor() { @Override public Message postProcessMessage(Message message) throws AmqpException { MessageProperties messageProperties = message.getMessageProperties(); //为每条消息设定过期时间 messageProperties.setExpiration(exp); return message; } }); . . .
- 消费者:user-queue的消费者注释,使消息无法被消费
@Slf4j @Component public class Consumer { /** * 正常用户队列消息监听消费者 * * @param user * @param message * @param channel @RabbitListener(queues = "${app.rabbitmq.queue.user}") public void userConsumer(User user, Message message, Channel channel) { log.info("正常用户业务监听:接收到消息:[{}]", JSON.toJSONString(user)); try { //参数为:消息的DeliveryTag,是否批量拒绝,是否重新入队 channel.basicNack(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false, false); log.info("拒绝签收...消息的路由键为:[{}]", message.getMessageProperties().getReceivedRoutingKey()); } catch (IOException e) { log.error("消息拒绝签收失败", e); } } */ /** * @param user * @param message * @param channel */ @RabbitListener(queues = "${app.rabbitmq.queue.user-dead-letter}") public void userDeadLetterConsumer(User user, Message message, Channel channel) { log.info("接收到死信消息:[{}]", JSON.toJSONString(user)); try { channel.basicAck(message.getMessageProperties().getDeliveryTag(), false); log.info("死信队列签收消息....消息路由键为:[{}]", message.getMessageProperties().getReceivedRoutingKey()); } catch (IOException e) { log.error("死信队列消息签收失败", e); } } }
场景三:队列达到最大消息数量(x-max-length)
- RabbitMQ 配置类:为队列设置最大消息数量x-max-length
. . . /** * 用户队列 * * @param userQueueName 用户队列名 * @return */ @Bean public Queue userQueue(@Value("${app.rabbitmq.queue.user}") String userQueueName, @Value("${app.rabbitmq.exchange.common-dead-letter}") String commonDeadLetterExchange) { return QueueBuilder .durable(userQueueName) //声明该队列的死信消息发送到的 交换机 (队列添加了这个参数之后会自动与该交换机绑定,并设置路由键,不需要开发者手动设置) .withArgument("x-dead-letter-exchange", commonDeadLetterExchange) //声明该队列死信消息在交换机的 路由键 .withArgument("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "user-dead-letter-routing-key") //队列最大消息数量 .withArgument("x-max-length", 2) .build(); } . . .
- 生产者:向队列中投递多条消息;
- 当投递第 3 条消息的时候,RabbitMQ 会把在最靠近被消费那一端的消息移出队列,并投递到死信队列。