“SpringBoot:快速入门”的版本间差异
(→实例) |
(→实例) |
||
| (未显示同一用户的6个中间版本) | |||
| 第99行: | 第99行: | ||
<version>4.3.7.RELEASE</version> | <version>4.3.7.RELEASE</version> | ||
</dependency> | </dependency> | ||
<!-- 连接池 --> | <!-- 连接池 --> | ||
<dependency> | <dependency> | ||
| 第106行: | 第107行: | ||
</dependency> | </dependency> | ||
</dependencies> | </dependencies> | ||
<build> | <build> | ||
<finalName>${project.artifactId}</finalName> | <finalName>${project.artifactId}</finalName> | ||
| 第117行: | 第119行: | ||
</configuration> | </configuration> | ||
</plugin> | </plugin> | ||
<!-- java编译插件 --> | <!-- java编译插件 --> | ||
<plugin> | <plugin> | ||
| 第128行: | 第131行: | ||
</plugin> | </plugin> | ||
</plugins> | </plugins> | ||
<pluginManagement> | <pluginManagement> | ||
<plugins> | <plugins> | ||
| 第154行: | 第158行: | ||
# 编写UserDao接口: | # 编写UserDao接口: | ||
#: <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | #: <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
public interface | public interface UserDao { | ||
//根据id查询用户信息 | //根据id查询用户信息 | ||
public User findUserById(int id) throws Exception; | public User findUserById(int id) throws Exception; | ||
| 第162行: | 第166行: | ||
#: <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | #: <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao { | public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao { | ||
// 需要向dao实现类中注入SqlSessionFactory | // 需要向dao实现类中注入SqlSessionFactory | ||
// 这里通过构造方法注入 | // 这里通过构造方法注入 | ||
| 第187行: | 第190行: | ||
@Service | @Service | ||
public class UserService { | public class UserService { | ||
@Autowired // 注入Spring容器中的bean对象 | @Autowired // 注入Spring容器中的bean对象 | ||
private UserDaoImpl UserDaoImpl; | private UserDaoImpl UserDaoImpl; | ||
| 第202行: | 第204行: | ||
@ComponentScan(basePackages = "cn.itcast.springboot.javaconfig") //配置扫描包 | @ComponentScan(basePackages = "cn.itcast.springboot.javaconfig") //配置扫描包 | ||
public class SpringConfig { | public class SpringConfig { | ||
@Bean // 通过该注解来表明是一个Bean对象,相当于xml中的<bean> | @Bean // 通过该注解来表明是一个Bean对象,相当于xml中的<bean> | ||
public UserDao getUserDao(){ | public UserDao getUserDao(){ | ||
| 第212行: | 第213行: | ||
#: <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | #: <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
public class Main { | public class Main { | ||
public static void main(String[] args) { | public static void main(String[] args) { | ||
// | // 使用xml方式的“加载spring配置文件” | ||
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml"); | |||
// 对比使用:通过Java配置来实例化Spring容器 | |||
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); | AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); | ||
// 使用xml方式的“根据配置创建对象” | |||
// | |||
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService"); | UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService"); | ||
// 对比使用:在Spring容器中获取Bean对象 | |||
// | |||
UserService userService = context.getBean(UserService.class); | UserService userService = context.getBean(UserService.class); | ||
| 第268行: | 第268行: | ||
=== 快速入门 === | === 快速入门 === | ||
==== 设置spring boot的parent ==== | ==== 设置spring boot的parent ==== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang=" | <syntaxhighlight lang="xml"> | ||
<parent> | <parent> | ||
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> | <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> | ||
| 第278行: | 第278行: | ||
==== 导入spring boot的web支持 ==== | ==== 导入spring boot的web支持 ==== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang=" | <syntaxhighlight lang="xml"> | ||
<dependencies> | <dependencies> | ||
<dependency> | <dependency> | ||
| 第288行: | 第288行: | ||
==== 添加Spring boot的插件 ==== | ==== 添加Spring boot的插件 ==== | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang=" | <syntaxhighlight lang="xml"> | ||
<build> | <build> | ||
<finalName>${project.artifactId}</finalName> | <finalName>${project.artifactId}</finalName> | ||
| 第335行: | 第335行: | ||
== SpringBoot核心 == | == SpringBoot核心 == | ||
=== 入口类和@SpringBootApplication === | |||
Spring Boot的项目一般都会有“xxxApplication”的入口类,类中有main方法,这是一个标准的Java应用程序的入口方法。<br/> | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@Controller | |||
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = { RedisAutoConfiguration.class }) | |||
@Configuration | |||
public class HelloApplication { | |||
public static void main(String[] args) { | |||
SpringApplication.run(HelloApplication.class, args); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
其中:“'''@SpringBootApplication'''”:是Spring Boot的核心注解,它其实是一个组合注解: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) | |||
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) | |||
@Documented | |||
@Inherited | |||
@SpringBootConfiguration | |||
@EnableAutoConfiguration | |||
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { | |||
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class), | |||
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) }) | |||
public @interface SpringBootApplication { | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
# “'''@SpringBootConfiguration'''”:Spring Boot项目的'''配置'''注解(组合注解): | |||
#: <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) | |||
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) | |||
@Documented | |||
@Configuration | |||
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration { | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
#* 在Spring Boot中推荐使用“@SpringBootConfiguration”替代“@Configuration”; | |||
# “'''@EnableAutoConfiguration'''”:'''启用自动配置''',该注解会使Spring Boot根据项目中依赖的jar包自动配置项目的配置项: | |||
# “'''@ComponentScan'''”:默认扫描“@SpringBootApplication”所在类的同级目录,以及它的子目录; | |||
=== 关闭自动配置 === | |||
启用自动配置时,Spring Boot会根据项目中的jar包依赖,自动做出配置;而Spring Boot支持的自动配置如下(非常多): | |||
:[[File:SpringBoot启动应用:自动配置.png|400px]] | |||
如果不需要Spring Boot自动配置,想关闭某一项的自动配置(以Redis为例): | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@Controller | |||
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = { RedisAutoConfiguration.class }) | |||
@Configuration | |||
public class HelloApplication { | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=== 自定义Banner === | |||
启动Spring Boot项目后会看到默认的Banner: | |||
:[[File:SpringBoot启动应用:Banner.png|600px]] | |||
* 关闭Banner: | |||
*: <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
public static void main(String[] args) { | |||
// SpringApplication.run(HelloApplication.class, args); | |||
SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(HelloApplication.class); | |||
application.setBannerMode(Mode.OFF); | |||
application.run(args); | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
* 自定义Banner: | |||
*# 在[http://patorjk.com/software/taag/#p=display&h=3&v=3&f=4Max&t=itcast%20Spring%20Boot 工具站点]中生成Banner,并保存为“banner.txt”; | |||
*# 将banner.txt拷贝到项目的resources目录; | |||
*#: [[File:SpringBoot启动应用:Banner自定义.png|200px]] | |||
=== 全局配置文件 === | |||
Spring Boot项目使用一个全局的配置文件“application.properties”(或“application.yml”),在“resources”目录下(或:类路径下的“/config”下)。<br/> | |||
可以进行项目全局配置,如: | |||
: <syntaxhighlight lang="properties"> | |||
server.port=8088 | |||
server.servlet-path=/ | |||
spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/public/ | |||
logging.level.org.springframework=DEBUG | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
* 更多配置:'''[[SpringBoot全局配置]]''' | |||
=== Starter pom === | |||
Starter POMs是可以包含到应用中的一个方便的“依赖关系描述符集合”。 | |||
* 可以通过starters获取所有Spring及相关技术的一站式服务,而不需要翻阅示例代码,拷贝粘贴大量的依赖描述符; | |||
* 所有的starters遵循一个相似的命名模式:“'''spring-boot-starter-*'''”; | |||
例如:在 SpringBoot 项目中集成 Redis,那么我只需要加入“spring-data-redis-starter”的依赖: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="xml"> | |||
<dependency> | |||
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> | |||
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> | |||
</dependency> | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
而不需考虑与其他内容的依赖、版本等; | |||
官方支持的 starter pom:(2.3.5.RELEASE) | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! 名称 !! 描述 | |||
|- | |||
! colspan="2"| application starters | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter || Core starter, including auto-configuration support, logging and YAML | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-activemq || Starter for JMS messaging using Apache ActiveMQ | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-amqp || Starter for using Spring AMQP and Rabbit MQ | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-aop || Starter for aspect-oriented programming with Spring AOP and AspectJ | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-artemis || Starter for JMS messaging using Apache Artemis | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-batch || Starter for using Spring Batch | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-cache || Starter for using Spring Framework’s caching support | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-data-cassandra || Starter for using Cassandra distributed database and Spring Data Cassandra | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-data-cassandra-reactive || Starter for using Cassandra distributed database and Spring Data Cassandra Reactive | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-data-couchbase || Starter for using Couchbase document-oriented database and Spring Data Couchbase | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-data-couchbase-reactive || Starter for using Couchbase document-oriented database and Spring Data Couchbase Reactive | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch || Starter for using Elasticsearch search and analytics engine and Spring Data Elasticsearch | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc || Starter for using Spring Data JDBC | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-data-jpa || Starter for using Spring Data JPA with Hibernate | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-data-ldap || Starter for using Spring Data LDAP | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb || Starter for using MongoDB document-oriented database and Spring Data MongoDB | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb-reactive || Starter for using MongoDB document-oriented database and Spring Data MongoDB Reactive | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-data-neo4j || Starter for using Neo4j graph database and Spring Data Neo4j | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-data-r2dbc || Starter for using Spring Data R2DBC | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-data-redis || Starter for using Redis key-value data store with Spring Data Redis and the Lettuce client | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-data-redis-reactive || Starter for using Redis key-value data store with Spring Data Redis reactive and the Lettuce client | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-data-rest || Starter for exposing Spring Data repositories over REST using Spring Data REST | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-data-solr || Starter for using the Apache Solr search platform with Spring Data Solr | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-freemarker || Starter for building MVC web applications using FreeMarker views | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-groovy-templates || Starter for building MVC web applications using Groovy Templates views | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-hateoas || Starter for building hypermedia-based RESTful web application with Spring MVC and Spring HATEOAS | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-integration || Starter for using Spring Integration | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-jdbc || Starter for using JDBC with the HikariCP connection pool | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-jersey || Starter for building RESTful web applications using JAX-RS and Jersey. An alternative to spring-boot-starter-web | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-jooq || Starter for using jOOQ to access SQL databases. An alternative to spring-boot-starter-data-jpa or spring-boot-starter-jdbc | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-json || Starter for reading and writing json | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-jta-atomikos || Starter for JTA transactions using Atomikos | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-jta-bitronix || Starter for JTA transactions using Bitronix. Deprecated since 2.3.0 | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-mail || Starter for using Java Mail and Spring Framework’s email sending support | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-mustache || Starter for building web applications using Mustache views | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client || Starter for using Spring Security’s OAuth2/OpenID Connect client features | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-oauth2-resource-server || Starter for using Spring Security’s OAuth2 resource server features | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-quartz || Starter for using the Quartz scheduler | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-rsocket || Starter for building RSocket clients and servers | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-security || Starter for using Spring Security | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-test || Starter for testing Spring Boot applications with libraries including JUnit, Hamcrest and Mockito | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf || Starter for building MVC web applications using Thymeleaf views | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-validation || Starter for using Java Bean Validation with Hibernate Validator | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-web || Starter for building web, including RESTful, applications using Spring MVC. Uses Tomcat as the default embedded container | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-web-services || Starter for using Spring Web Services | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-webflux || Starter for building WebFlux applications using Spring Framework’s Reactive Web support | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-websocket || Starter for building WebSocket applications using Spring Framework’s WebSocket support | |||
|- | |||
! colspan="2"| production starters | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-actuator || Starter for using Spring Boot’s Actuator which provides production ready features to help you monitor and manage your application | |||
|- | |||
! colspan="2"| technical starters | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-jetty || Starter for using Jetty as the embedded servlet container. An alternative to spring-boot-starter-tomcat | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-log4j2 || Starter for using Log4j2 for logging. An alternative to spring-boot-starter-logging | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-logging || Starter for logging using Logback. Default logging starter | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-reactor-netty || Starter for using Reactor Netty as the embedded reactive HTTP server. | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-tomcat || Starter for using Tomcat as the embedded servlet container. Default servlet container starter used by spring-boot-starter-web | |||
|- | |||
| spring-boot-starter-undertow || Starter for using Undertow as the embedded servlet container. An alternative to spring-boot-starter-tomcat | |||
|} | |||
=== Xml 配置文件 === | |||
# “'''@PropertySource'''”:加载指定的配置文件; | |||
#* 只能加载“*.properties”文件,不能加载“.yaml”文件; | |||
#: <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@PropertySource(value = { "classpath:jdbc.properties" }, ignoreResourceNotFound = true) | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
# “'''@Import'''”: | |||
#* 4.2之前,只支持导入配置类;(相当于“<import resource=""/>”标签) | |||
#* 4.2之后,支持导入普通的java类,并将其声明成一个bean; | |||
#: <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@Import({ CustomerConfig.class, SchedulerConfig.class }) | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
# “'''@ImportResource'''”:导入Spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效; | |||
#* SpringBoot中编写的Spring配置文件是不能自动识别的;【???】 | |||
#: <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:applicationContext.xml"}) | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=== 日志 === | |||
Spring Boot对各种日志框架都做了支持,可以通过全局配置来修改默认的日志的配置: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="properties"> | |||
#设置日志级别 | |||
logging.level.*= # Log levels severity mapping. For instance `logging.level.org.springframework=DEBUG` | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
== 自动配置的原理 == | == 自动配置的原理 == | ||
Spring Boot在进行SpringApplication对象实例化时会加载“META-INF/spring.factories”文件,将该配置文件中的配置载入到Spring容器。 | |||
* “META-INF/spring.factories”文件,位于“'''spring-boot-autoconfigure-1.5.2.RELEASE.jar'''”包中,而非项目路径下; | |||
*: [[File:spring-boot-autoconfigure-1.5.2.RELEASE包中.jpg|400px]] | |||
* 全局配置“application.properties”(“application.yml”)时,需要的配置项,可以根据jar包(“org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure”)下对应包中的自动配置类得出; | |||
*: 如下面的 Redis的自动配置; | |||
=== spring.factories 的加载 === | |||
配置文件“spring.factories”的读取,是在“org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication”的初始化方法中进行的: | |||
: <syntaxhighlight lang="java" line highlight="9,15,20"> | |||
public class SpringApplication { | |||
... | |||
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" }) | |||
private void initialize(Object[] sources) { | |||
if (sources != null && sources.length > 0) { | |||
this.sources.addAll(Arrays.asList(sources)); | |||
} | |||
this.webEnvironment = deduceWebEnvironment(); | |||
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class)); | |||
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)); | |||
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass(); | |||
} | |||
... | |||
private <T> Collection<? extends T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) { | |||
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {}); | |||
} | |||
private <T> Collection<? extends T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) { | |||
ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); | |||
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates | |||
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<String>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader)); | |||
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names); | |||
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances); | |||
return instances; | |||
} | |||
... | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
“org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader”: | |||
: <syntaxhighlight lang="java" line highlight="3,8"> | |||
public abstract class SpringFactoriesLoader { | |||
... | |||
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories"; | |||
... | |||
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) { | |||
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName(); | |||
try { | |||
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION)); | |||
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>(); | |||
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) { | |||
URL url = urls.nextElement(); | |||
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(url)); | |||
String factoryClassNames = properties.getProperty(factoryClassName); | |||
result.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(factoryClassNames))); | |||
} | |||
return result; | |||
} | |||
catch (IOException ex) { | |||
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load [" + factoryClass.getName() + "] factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex); | |||
} | |||
} | |||
... | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
=== 示例:Redis的自动配置 === | |||
由“spring.factories”文件: | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="properties" highlight="4"> | |||
# Auto Configure | |||
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\ | |||
... | |||
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\ | |||
... | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
可知“org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration”是Redis的自动配置: | |||
:[[File:spring-boot:RedisAutoConfiguration.jpg|300px]] | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@Configuration | |||
@ConditionalOnClass({ JedisConnection.class, RedisOperations.class, Jedis.class }) | |||
@EnableConfigurationProperties(RedisProperties.class) | |||
public class RedisAutoConfiguration { | |||
@Configuration | |||
@ConditionalOnClass(GenericObjectPool.class) | |||
protected static class RedisConnectionConfiguration { | |||
private final RedisProperties properties; | |||
private final RedisSentinelConfiguration sentinelConfiguration; | |||
private final RedisClusterConfiguration clusterConfiguration; | |||
... | |||
} | |||
@Configuration | |||
protected static class RedisConfiguration { | |||
@Bean | |||
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "redisTemplate") | |||
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate( | |||
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) | |||
throws UnknownHostException { | |||
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<Object, Object>(); | |||
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); | |||
return template; | |||
} | |||
@Bean | |||
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(StringRedisTemplate.class) | |||
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate( | |||
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) | |||
throws UnknownHostException { | |||
StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate(); | |||
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); | |||
return template; | |||
} | |||
} | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
# 内部类“RedisConnectionConfiguration”:Redis连接设置; | |||
#* “RedisProperties”:Redis配置类; | |||
# 内部类“RedisConfiguration”:获取RedisTemplate; | |||
* “RedisProperties”: | |||
*:<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.redis") | |||
public class RedisProperties { | |||
/** | |||
* Database index used by the connection factory. | |||
*/ | |||
private int database = 0; | |||
/** | |||
* Redis url, which will overrule host, port and password if set. | |||
*/ | |||
private String url; | |||
/** | |||
* Redis server host. | |||
*/ | |||
private String host = "localhost"; | |||
/** | |||
* Login password of the redis server. | |||
*/ | |||
private String password; | |||
... | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
*# “(prefix = "spring.redis")”:配置项的前缀(匹配SpringBoot全局配置文件中的前缀); | |||
*# “database”、“url”等:配置项; | |||
=== 条件注解 === | |||
SpringBoot内部提供了特有的注解:条件注解(Conditional Annotation);<br/> | |||
条件注解存在的意义在于动态识别(也可以说是代码自动化执行)。比如@ConditionalOnClass会检查类加载器中是否存在对应的类,如果有的话被注解修饰的类就有资格被Spring容器所注册,否则会被skip。 | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
! 条件注解 | |||
! 对应的Condition处理类 | |||
! 说明 | |||
|- | |||
| @ConditionalOnBean || OnBeanCondition | |||
| Spring容器中是否存在对应的实例。 | |||
* 可以通过实例的类型、类名、注解、昵称去容器中查找; | |||
* (可以配置从当前容器中查找或者父容器中查找或者两者一起查找); | |||
* 这些属性都是数组,通过”与”的关系进行查找; | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@ConditionalOnBean(javax.sql.DataSource.class) | |||
// Spring容器或者所有父容器中需要存在至少一个javax.sql.DataSource类的实例 | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|- | |||
| @ConditionalOnClass || OnClassCondition | |||
| 类加载器中是否存在对应的类。 | |||
* 可以通过Class指定(value属性)或者Class的全名指定(name属性); | |||
* 如果是多个类或者多个类名的话,关系是”与”关系,也就是说这些类或者类名都必须同时在类加载器中存在; | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@ConditionalOnClass({ Configuration.class, FreeMarkerConfigurationFactory.class }) | |||
// 类加载器中必须存在 Configuration和 FreeMarkerConfigurationFactory这两个类 | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|- | |||
| @ConditionalOnExpression || OnExpressionCondition | |||
| 判断SpEL 表达式是否成立 | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@ConditionalOnExpression("'${server.host}'=='localhost'") | |||
// server.host配置项的值需要是localhost | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|- | |||
| @ConditionalOnJava || OnJavaCondition | |||
| 指定Java版本是否符合要求。 | |||
* 内部有2个属性“value”和“range”: | |||
*# value表示一个枚举的Java版本, | |||
*# range表示比这个老或者新于等于指定的Java版本(默认是新于等于)。 | |||
* 内部会基于某些jdk版本特有的类去类加载器中查询,比如: | |||
*# 如果是jdk9,类加载器中需要存在“java.security.cert.URICertStoreParameters”; | |||
*# 如果是jdk8,类加载器中需要存在“java.util.function.Function”; | |||
*# 如果是jdk7,类加载器中需要存在“java.nio.file.Files”; | |||
*# 如果是jdk6,类加载器中需要存在“java.util.ServiceLoader” | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
ConditionalOnJava(JavaVersion.EIGHT) | |||
// Java版本至少是8 | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|- | |||
| @ConditionalOnMissingBean || OnBeanCondition | |||
| Spring容器中是否缺少对应的实例。 | |||
* 可以通过实例的类型、类名、注解、昵称去容器中查找 | |||
*: (可以配置从当前容器中查找或者父容器中查找或者两者一起查找) | |||
* 这些属性都是数组,通过”与”的关系进行查找。 | |||
* 还多了2个属性ignored(类名)和ignoredType(类名),匹配的过程中会忽略这些bean | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorController.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT) | |||
// Spring当前容器中不存在ErrorController类型的bean | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|- | |||
| @ConditionalOnMissingClass || OnClassCondition | |||
| 跟ConditionalOnClass的处理逻辑一样,只是条件相反,在类加载器中不存在对应的类 | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@ConditionalOnMissingClass("GenericObjectPool") | |||
// 类加载器中不能存在GenericObjectPool这个类 | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|- | |||
| @ConditionalOnNotWebApplication || OnWebApplicationCondition | |||
| 应用程序是否是非Web程序,没有提供属性,只是一个标识。 | |||
* 会从判断Web程序特有的类是否存在,环境是否是Servlet环境,容器是否是Web容器等 | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication | |||
// 必须在非Web应用下才会生效 | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|- | |||
| @ConditionalOnProperty || OnPropertyCondition | |||
| 应用环境中的屬性是否存在。 | |||
* 提供“prefix”、“name”、“havingValue”以及“matchIfMissing”属性。 | |||
*: prefix:属性名的前缀, | |||
*: name:属性名, | |||
*: havingValue:具体的属性值, | |||
*: matchIfMissing:(boolean值)如果属性不存在,这个matchIfMissing为true的话,会继续验证下去,否则属性不存在的话直接就相当于匹配不成功; | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "auto", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true) | |||
// 应用程序的环境中必须有spring.aop.auto这项配置,且它的值是true或者环境中不存在spring.aop.auto配置(matchIfMissing为true) | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|- | |||
| @ConditionalOnResource || OnResourceCondition | |||
| 是否存在指定的资源文件。 | |||
* 只有一个属性resources,是个String数组。会从类加载器中去查询对应的资源文件是否存在; | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@ConditionalOnResource(resources="mybatis.xml") | |||
// 类加载路径中必须存在mybatis.xml文件 | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|- | |||
| @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate || OnBeanCondition | |||
| Spring容器中是否存在且只存在一个对应的实例。 | |||
* 只有3个属性“value”、“type”、“search”,跟ConditionalOnBean中的这3种属性值意义一样 | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(PlatformTransactionManager.class) | |||
// Spring当前或父容器中必须存在PlatformTransactionManager这个类型的实例,且只有一个实例 | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|- | |||
| @ConditionalOnWebApplication || OnWebApplicationCondition | |||
| 应用程序是否是Web程序,没有提供属性,只是一个标识。 | |||
* 会从判断Web程序特有的类是否存在,环境是否是Servlet环境,容器是否是Web容器等 | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
@ConditionalOnWebApplication | |||
// 必须在Web应用下才会生效 | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
|} | |||
=== Maven下载源码 === | |||
通过“dependency:sources”命令,可以下载该项目中所有的依赖的包的源码。 | |||
2021年11月8日 (一) 23:34的最新版本
Spring的发展
- Spring1.x:
- 通过xml文件配置bean:随着项目的不断扩大,需要将xml配置分放到不同的配置文件中,需要频繁的在java类和xml配置文件中切换。
- Spring2.x:
- (JDK 1.5 注解支持)使用注解对Bean进行申明和注入:大大的减少了xml配置文件,同时也大大简化了项目的开发。
- 应用的基本配置用xml(如:数据源、资源文件等);
- 业务开发用注解(如:Service中注入bean等);
- Spring3.x(Spring4.x):
- 推荐使用Java配置方式:可以完全替代xml配置。
Spring的Java配置方式
(Java配置是Spring4.x推荐的配置方式)
Spring的Java配置方式是通过 @Configuration 和 @Bean 这两个注解实现的:
- @Configuration:标记类,相当于一个xml配置文件;
- @Bean:标记方法,相当于xml配置中的“<bean>”;
其他配置类注解:
- 读取外部的资源配置文件:
- @PropertySource:指定读取的配置文件;
- @Value:获取配置文件的配置项;
示例:配置数据库连接池:
// 通过该注解来表明该类是一个Spring的配置,相当于一个xml文件 @Configuration // 配置扫描包,相当于xml中的"<context:component-scan ...>" @ComponentScan(basePackages = "cn.itcast.springboot.javaconfig") //加载配置文件 @PropertySource(value = { "classpath:jdbc.properties", "xxx.properties" }, ignoreResourceNotFound = true) public class SpringConfig { @Bean // 通过该注解来表明是一个Bean对象,相当于xml中的<bean> //1、相当于xml中的<bean>标签 //2、相当于类中的@Service类的注解 //所以"UserDAO"可以用于"UserService"属性注入 public UserDAO getUserDAO() { return new UserDAO(); // 直接new对象做演示 } //返回值,相当于<bean>中的"class"属性 //方法名称,相当于<bean>中的"id"属性? // 获取配置文件的配置项 @Value("${jdbc.url}") private String jdbcUrl; @Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}") private String jdbcDriverClassName; @Value("${jdbc.username}") private String jdbcUsername; @Value("${jdbc.password}") private String jdbcPassword; @Bean(destroyMethod = "close") public DataSource dataSource() { BoneCPDataSource boneCPDataSource = new BoneCPDataSource(); // 数据库驱动 boneCPDataSource.setDriverClass(jdbcDriverClassName); // 相应驱动的jdbcUrl boneCPDataSource.setJdbcUrl(jdbcUrl); // 数据库的用户名 boneCPDataSource.setUsername(jdbcUsername); // 数据库的密码 boneCPDataSource.setPassword(jdbcUsername); // 检查数据库连接池中空闲连接的间隔时间,单位是分,默认值:240,如果要取消则设置为0 boneCPDataSource.setIdleConnectionTestPeriodInMinutes(60); // 连接池中未使用的链接最大存活时间,单位是分,默认值:60,如果要永远存活设置为0 boneCPDataSource.setIdleMaxAgeInMinutes(30); // 每个分区最大的连接数 boneCPDataSource.setMaxConnectionsPerPartition(100); // 每个分区最小的连接数 boneCPDataSource.setMinConnectionsPerPartition(5); return boneCPDataSource; } }
实例
- 创建工程以及导入依赖:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <groupId>cn.itcast.springboot</groupId> <artifactId>itcast-springboot</artifactId> <version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOT</version> <packaging>war</packaging> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>4.3.7.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <!-- 连接池 --> <dependency> <groupId>com.jolbox</groupId> <artifactId>bonecp-spring</artifactId> <version>0.8.0.RELEASE</version> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <finalName>${project.artifactId}</finalName> <plugins> <!-- 资源文件拷贝插件 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <encoding>UTF-8</encoding> </configuration> </plugin> <!-- java编译插件 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <source>1.7</source> <target>1.7</target> <encoding>UTF-8</encoding> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> <pluginManagement> <plugins> <!-- 配置Tomcat插件 --> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId> <artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.2</version> </plugin> </plugins> </pluginManagement> </build> </project>
- 编写User对象:
public class User { private String username; private String password; private Integer age; // getter & setter & toString }
- 编写UserDao接口:
public interface UserDao { //根据id查询用户信息 public User findUserById(int id) throws Exception; }
- 编写UserDaoImpl接口:(mybatis)
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao { // 需要向dao实现类中注入SqlSessionFactory // 这里通过构造方法注入 private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory; public UserDaoImpl(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) { this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory; } @Override public User findUserById(int id) throws Exception { SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); User user = sqlSession.selectOne("test.findUserById", id); // 释放资源 sqlSession.close(); return user; } }
- 编写UserService实现User数据操作业务逻辑:
@Service public class UserService { @Autowired // 注入Spring容器中的bean对象 private UserDaoImpl UserDaoImpl; public User findUserById(int id) throws Exception { // 调用userDAO中的方法进行查询 return this.UserDaoImpl.findUserById(id); } }
- 编写SpringConfig用于实例化Spring容器:
@Configuration //通过该注解来表明该类是一个Spring的配置,相当于一个xml文件 @ComponentScan(basePackages = "cn.itcast.springboot.javaconfig") //配置扫描包 public class SpringConfig { @Bean // 通过该注解来表明是一个Bean对象,相当于xml中的<bean> public UserDao getUserDao(){ return new UserDao(); // 直接new对象做演示 } }
- 编写测试方法,启动Spring容器:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // 使用xml方式的“加载spring配置文件” ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml"); // 对比使用:通过Java配置来实例化Spring容器 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class); // 使用xml方式的“根据配置创建对象” UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService"); // 对比使用:在Spring容器中获取Bean对象 UserService userService = context.getBean(UserService.class); // 调用对象中的方法 List<User> list = userService.queryUserList(); for (User user : list) { System.out.println(user.getUsername() + ", " + user.getPassword() + ", " + user.getPassword()); } // 销毁该容器 context.destroy(); } }
实例化Spring容器:xml与Java配置
对比,“xml、注解”于“Java配置类”的实例化Spring容器:
// 通过Java配置来实例化Spring容器
// 1、Java配置类
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
// 2、xml、注解
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 在Spring容器中“获取Bean对象”
// 1、Java配置类
UserService userService = context.getBean(UserService.class);
// 2、xml、注解
UserService userService = (UserService) context.getBean("userService");
Spring Boot
“习惯优于配置”:
SpringBoot是一种全新的框架,目的是为了简化Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。该框架使用特定的方式(集成starter,约定优于配置)来进行配置,从而使开发人员不需要再定义样板化的配置。
- SpringBoot基于Sring4进行设计,继承了原有Spring框架的优秀基因。
- SpringBoot并不是一个框架,而是一些类库的集合。
- maven或者gradle项目导入相应依赖即可使用SpringBoot,而无需自行管理这些类库的版本。
优点:
- 快速创建基于Spring的应用程序。
- 无需手动管理依赖包的版本。
- 自动配置,无需XML。
- 嵌入式的Tomcat,无需部署war文件。
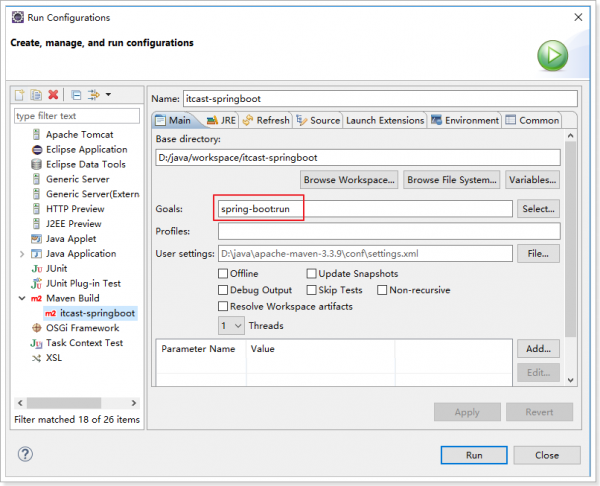
快速入门
设置spring boot的parent
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.2.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
Spring boot的项目必须要将parent设置为spring boot的parent,该parent包含了大量默认的配置,大大简化了我们的开发。
导入spring boot的web支持
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
添加Spring boot的插件
<build>
<finalName>${project.artifactId}</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<pluginManagement>
...
</pluginManagement>
</build>
编写第一个Spring Boot的应用
@Controller
@SpringBootApplication
@Configuration
public class HelloApplication {
@RequestMapping("hello")
@ResponseBody
public String hello(){
return "hello world!";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloApplication.class, args);
}
}
- @SpringBootApplication:Spring Boot项目的核心注解,主要目的是开启自动配置;
- @Configuration:这是一个配置Spring的配置类;
- @Controller:标明这是一个SpringMVC的Controller控制器;
- main方法:在main方法中启动一个应用,即:这个应用的入口;
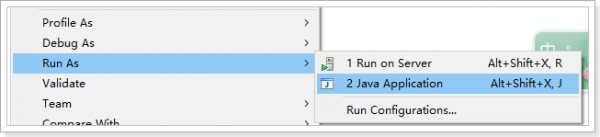
启动应用
在Spring Boot项目中,启动的方式有两种,一种是另外一种是。
SpringBoot核心
入口类和@SpringBootApplication
Spring Boot的项目一般都会有“xxxApplication”的入口类,类中有main方法,这是一个标准的Java应用程序的入口方法。
@Controller
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = { RedisAutoConfiguration.class })
@Configuration
public class HelloApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloApplication.class, args);
}
}
其中:“@SpringBootApplication”:是Spring Boot的核心注解,它其实是一个组合注解:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
- “@SpringBootConfiguration”:Spring Boot项目的配置注解(组合注解):
@Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Configuration public @interface SpringBootConfiguration { }
- 在Spring Boot中推荐使用“@SpringBootConfiguration”替代“@Configuration”;
- “@EnableAutoConfiguration”:启用自动配置,该注解会使Spring Boot根据项目中依赖的jar包自动配置项目的配置项:
- “@ComponentScan”:默认扫描“@SpringBootApplication”所在类的同级目录,以及它的子目录;
关闭自动配置
启用自动配置时,Spring Boot会根据项目中的jar包依赖,自动做出配置;而Spring Boot支持的自动配置如下(非常多):
如果不需要Spring Boot自动配置,想关闭某一项的自动配置(以Redis为例):
@Controller
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = { RedisAutoConfiguration.class })
@Configuration
public class HelloApplication {
自定义Banner
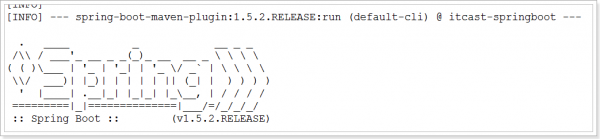
启动Spring Boot项目后会看到默认的Banner:
- 关闭Banner:
public static void main(String[] args) { // SpringApplication.run(HelloApplication.class, args); SpringApplication application = new SpringApplication(HelloApplication.class); application.setBannerMode(Mode.OFF); application.run(args); }
- 自定义Banner:
- 在工具站点中生成Banner,并保存为“banner.txt”;
- 将banner.txt拷贝到项目的resources目录;
全局配置文件
Spring Boot项目使用一个全局的配置文件“application.properties”(或“application.yml”),在“resources”目录下(或:类路径下的“/config”下)。
可以进行项目全局配置,如:
server.port=8088 server.servlet-path=/ spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/public/ logging.level.org.springframework=DEBUG
- 更多配置:SpringBoot全局配置
Starter pom
Starter POMs是可以包含到应用中的一个方便的“依赖关系描述符集合”。
- 可以通过starters获取所有Spring及相关技术的一站式服务,而不需要翻阅示例代码,拷贝粘贴大量的依赖描述符;
- 所有的starters遵循一个相似的命名模式:“spring-boot-starter-*”;
例如:在 SpringBoot 项目中集成 Redis,那么我只需要加入“spring-data-redis-starter”的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
而不需考虑与其他内容的依赖、版本等;
官方支持的 starter pom:(2.3.5.RELEASE)
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| application starters | |
| spring-boot-starter | Core starter, including auto-configuration support, logging and YAML |
| spring-boot-starter-activemq | Starter for JMS messaging using Apache ActiveMQ |
| spring-boot-starter-amqp | Starter for using Spring AMQP and Rabbit MQ |
| spring-boot-starter-aop | Starter for aspect-oriented programming with Spring AOP and AspectJ |
| spring-boot-starter-artemis | Starter for JMS messaging using Apache Artemis |
| spring-boot-starter-batch | Starter for using Spring Batch |
| spring-boot-starter-cache | Starter for using Spring Framework’s caching support |
| spring-boot-starter-data-cassandra | Starter for using Cassandra distributed database and Spring Data Cassandra |
| spring-boot-starter-data-cassandra-reactive | Starter for using Cassandra distributed database and Spring Data Cassandra Reactive |
| spring-boot-starter-data-couchbase | Starter for using Couchbase document-oriented database and Spring Data Couchbase |
| spring-boot-starter-data-couchbase-reactive | Starter for using Couchbase document-oriented database and Spring Data Couchbase Reactive |
| spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch | Starter for using Elasticsearch search and analytics engine and Spring Data Elasticsearch |
| spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc | Starter for using Spring Data JDBC |
| spring-boot-starter-data-jpa | Starter for using Spring Data JPA with Hibernate |
| spring-boot-starter-data-ldap | Starter for using Spring Data LDAP |
| spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb | Starter for using MongoDB document-oriented database and Spring Data MongoDB |
| spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb-reactive | Starter for using MongoDB document-oriented database and Spring Data MongoDB Reactive |
| spring-boot-starter-data-neo4j | Starter for using Neo4j graph database and Spring Data Neo4j |
| spring-boot-starter-data-r2dbc | Starter for using Spring Data R2DBC |
| spring-boot-starter-data-redis | Starter for using Redis key-value data store with Spring Data Redis and the Lettuce client |
| spring-boot-starter-data-redis-reactive | Starter for using Redis key-value data store with Spring Data Redis reactive and the Lettuce client |
| spring-boot-starter-data-rest | Starter for exposing Spring Data repositories over REST using Spring Data REST |
| spring-boot-starter-data-solr | Starter for using the Apache Solr search platform with Spring Data Solr |
| spring-boot-starter-freemarker | Starter for building MVC web applications using FreeMarker views |
| spring-boot-starter-groovy-templates | Starter for building MVC web applications using Groovy Templates views |
| spring-boot-starter-hateoas | Starter for building hypermedia-based RESTful web application with Spring MVC and Spring HATEOAS |
| spring-boot-starter-integration | Starter for using Spring Integration |
| spring-boot-starter-jdbc | Starter for using JDBC with the HikariCP connection pool |
| spring-boot-starter-jersey | Starter for building RESTful web applications using JAX-RS and Jersey. An alternative to spring-boot-starter-web |
| spring-boot-starter-jooq | Starter for using jOOQ to access SQL databases. An alternative to spring-boot-starter-data-jpa or spring-boot-starter-jdbc |
| spring-boot-starter-json | Starter for reading and writing json |
| spring-boot-starter-jta-atomikos | Starter for JTA transactions using Atomikos |
| spring-boot-starter-jta-bitronix | Starter for JTA transactions using Bitronix. Deprecated since 2.3.0 |
| spring-boot-starter-mail | Starter for using Java Mail and Spring Framework’s email sending support |
| spring-boot-starter-mustache | Starter for building web applications using Mustache views |
| spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client | Starter for using Spring Security’s OAuth2/OpenID Connect client features |
| spring-boot-starter-oauth2-resource-server | Starter for using Spring Security’s OAuth2 resource server features |
| spring-boot-starter-quartz | Starter for using the Quartz scheduler |
| spring-boot-starter-rsocket | Starter for building RSocket clients and servers |
| spring-boot-starter-security | Starter for using Spring Security |
| spring-boot-starter-test | Starter for testing Spring Boot applications with libraries including JUnit, Hamcrest and Mockito |
| spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf | Starter for building MVC web applications using Thymeleaf views |
| spring-boot-starter-validation | Starter for using Java Bean Validation with Hibernate Validator |
| spring-boot-starter-web | Starter for building web, including RESTful, applications using Spring MVC. Uses Tomcat as the default embedded container |
| spring-boot-starter-web-services | Starter for using Spring Web Services |
| spring-boot-starter-webflux | Starter for building WebFlux applications using Spring Framework’s Reactive Web support |
| spring-boot-starter-websocket | Starter for building WebSocket applications using Spring Framework’s WebSocket support |
| production starters | |
| spring-boot-starter-actuator | Starter for using Spring Boot’s Actuator which provides production ready features to help you monitor and manage your application |
| technical starters | |
| spring-boot-starter-jetty | Starter for using Jetty as the embedded servlet container. An alternative to spring-boot-starter-tomcat |
| spring-boot-starter-log4j2 | Starter for using Log4j2 for logging. An alternative to spring-boot-starter-logging |
| spring-boot-starter-logging | Starter for logging using Logback. Default logging starter |
| spring-boot-starter-reactor-netty | Starter for using Reactor Netty as the embedded reactive HTTP server. |
| spring-boot-starter-tomcat | Starter for using Tomcat as the embedded servlet container. Default servlet container starter used by spring-boot-starter-web |
| spring-boot-starter-undertow | Starter for using Undertow as the embedded servlet container. An alternative to spring-boot-starter-tomcat |
Xml 配置文件
- “@PropertySource”:加载指定的配置文件;
- 只能加载“*.properties”文件,不能加载“.yaml”文件;
@PropertySource(value = { "classpath:jdbc.properties" }, ignoreResourceNotFound = true)
- “@Import”:
- 4.2之前,只支持导入配置类;(相当于“<import resource=""/>”标签)
- 4.2之后,支持导入普通的java类,并将其声明成一个bean;
@Import({ CustomerConfig.class, SchedulerConfig.class })
- “@ImportResource”:导入Spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效;
- SpringBoot中编写的Spring配置文件是不能自动识别的;【???】
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:applicationContext.xml"})
日志
Spring Boot对各种日志框架都做了支持,可以通过全局配置来修改默认的日志的配置:
#设置日志级别
logging.level.*= # Log levels severity mapping. For instance `logging.level.org.springframework=DEBUG`
自动配置的原理
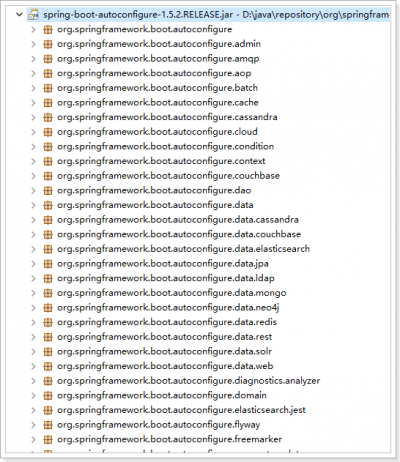
Spring Boot在进行SpringApplication对象实例化时会加载“META-INF/spring.factories”文件,将该配置文件中的配置载入到Spring容器。
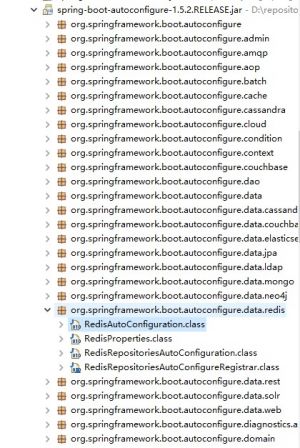
- “META-INF/spring.factories”文件,位于“spring-boot-autoconfigure-1.5.2.RELEASE.jar”包中,而非项目路径下;
- 全局配置“application.properties”(“application.yml”)时,需要的配置项,可以根据jar包(“org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure”)下对应包中的自动配置类得出;
- 如下面的 Redis的自动配置;
spring.factories 的加载
配置文件“spring.factories”的读取,是在“org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication”的初始化方法中进行的:
public class SpringApplication { ... @SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" }) private void initialize(Object[] sources) { if (sources != null && sources.length > 0) { this.sources.addAll(Arrays.asList(sources)); } this.webEnvironment = deduceWebEnvironment(); setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class)); setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class)); this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass(); } ... private <T> Collection<? extends T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) { return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {}); } private <T> Collection<? extends T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) { ClassLoader classLoader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); // Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<String>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader)); List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names); AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances); return instances; } ... }
“org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader”:
public abstract class SpringFactoriesLoader { ... public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories"; ... public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader) { String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName(); try { Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ? classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION)); List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>(); while (urls.hasMoreElements()) { URL url = urls.nextElement(); Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(new UrlResource(url)); String factoryClassNames = properties.getProperty(factoryClassName); result.addAll(Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(factoryClassNames))); } return result; } catch (IOException ex) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load [" + factoryClass.getName() + "] factories from location [" + FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex); } } ... }
示例:Redis的自动配置
由“spring.factories”文件:
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
...
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration,\
...
可知“org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration”是Redis的自动配置:
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ JedisConnection.class, RedisOperations.class, Jedis.class })
@EnableConfigurationProperties(RedisProperties.class)
public class RedisAutoConfiguration {
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(GenericObjectPool.class)
protected static class RedisConnectionConfiguration {
private final RedisProperties properties;
private final RedisSentinelConfiguration sentinelConfiguration;
private final RedisClusterConfiguration clusterConfiguration;
...
}
@Configuration
protected static class RedisConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "redisTemplate")
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory)
throws UnknownHostException {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<Object, Object>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(StringRedisTemplate.class)
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory)
throws UnknownHostException {
StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
}
}
- 内部类“RedisConnectionConfiguration”:Redis连接设置;
- “RedisProperties”:Redis配置类;
- 内部类“RedisConfiguration”:获取RedisTemplate;
- “RedisProperties”:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.redis") public class RedisProperties { /** * Database index used by the connection factory. */ private int database = 0; /** * Redis url, which will overrule host, port and password if set. */ private String url; /** * Redis server host. */ private String host = "localhost"; /** * Login password of the redis server. */ private String password; ... }
- “(prefix = "spring.redis")”:配置项的前缀(匹配SpringBoot全局配置文件中的前缀);
- “database”、“url”等:配置项;
条件注解
SpringBoot内部提供了特有的注解:条件注解(Conditional Annotation);
条件注解存在的意义在于动态识别(也可以说是代码自动化执行)。比如@ConditionalOnClass会检查类加载器中是否存在对应的类,如果有的话被注解修饰的类就有资格被Spring容器所注册,否则会被skip。
| 条件注解 | 对应的Condition处理类 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| @ConditionalOnBean | OnBeanCondition | Spring容器中是否存在对应的实例。
@ConditionalOnBean(javax.sql.DataSource.class)
// Spring容器或者所有父容器中需要存在至少一个javax.sql.DataSource类的实例
|
| @ConditionalOnClass | OnClassCondition | 类加载器中是否存在对应的类。
@ConditionalOnClass({ Configuration.class, FreeMarkerConfigurationFactory.class })
// 类加载器中必须存在 Configuration和 FreeMarkerConfigurationFactory这两个类
|
| @ConditionalOnExpression | OnExpressionCondition | 判断SpEL 表达式是否成立
@ConditionalOnExpression("'${server.host}'=='localhost'")
// server.host配置项的值需要是localhost
|
| @ConditionalOnJava | OnJavaCondition | 指定Java版本是否符合要求。
ConditionalOnJava(JavaVersion.EIGHT)
// Java版本至少是8
|
| @ConditionalOnMissingBean | OnBeanCondition | Spring容器中是否缺少对应的实例。
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(value = ErrorController.class, search = SearchStrategy.CURRENT)
// Spring当前容器中不存在ErrorController类型的bean
|
| @ConditionalOnMissingClass | OnClassCondition | 跟ConditionalOnClass的处理逻辑一样,只是条件相反,在类加载器中不存在对应的类
@ConditionalOnMissingClass("GenericObjectPool")
// 类加载器中不能存在GenericObjectPool这个类
|
| @ConditionalOnNotWebApplication | OnWebApplicationCondition | 应用程序是否是非Web程序,没有提供属性,只是一个标识。
@ConditionalOnNotWebApplication
// 必须在非Web应用下才会生效
|
| @ConditionalOnProperty | OnPropertyCondition | 应用环境中的屬性是否存在。
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "auto", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
// 应用程序的环境中必须有spring.aop.auto这项配置,且它的值是true或者环境中不存在spring.aop.auto配置(matchIfMissing为true)
|
| @ConditionalOnResource | OnResourceCondition | 是否存在指定的资源文件。
@ConditionalOnResource(resources="mybatis.xml")
// 类加载路径中必须存在mybatis.xml文件
|
| @ConditionalOnSingleCandidate | OnBeanCondition | Spring容器中是否存在且只存在一个对应的实例。
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(PlatformTransactionManager.class)
// Spring当前或父容器中必须存在PlatformTransactionManager这个类型的实例,且只有一个实例
|
| @ConditionalOnWebApplication | OnWebApplicationCondition | 应用程序是否是Web程序,没有提供属性,只是一个标识。
@ConditionalOnWebApplication
// 必须在Web应用下才会生效
|
Maven下载源码
通过“dependency:sources”命令,可以下载该项目中所有的依赖的包的源码。