“动态代理、CGLIB 与 切面编程”的版本间差异
跳到导航
跳到搜索
(→常用的API) |
|||
| 第267行: | 第267行: | ||
| Enhancer创建一个被代理对象的子类并且拦截所有的方法调用(包括从Object中继承的toString和hashCode方法) | | Enhancer创建一个被代理对象的子类并且拦截所有的方法调用(包括从Object中继承的toString和hashCode方法) | ||
* 作用类似Proxy类;但Enhancer既能够代理普通的class,也能够代理接口;(不能代理final方法) | * 作用类似Proxy类;但Enhancer既能够代理普通的class,也能够代理接口;(不能代理final方法) | ||
# | # “Enhancer.setSuperclass()”:设置父类型; | ||
# | # “Enhancer.create(Object…)”:创建增强对象; | ||
# | # “Enhancer.createClass()”:创建字节码(.class); | ||
# setCallback() | # “Enhancer.setCallback()”:设置回调; | ||
#* | #* “'''InvocationHandler'''”可以作为回调,但必须防止死循环; | ||
#*:(invoke中调用的任何原代理类方法,均会重新代理到invoke方法中) | #*:(invoke中调用的任何原代理类方法,均会重新代理到invoke方法中) | ||
#* | #* “'''MethodInterceptor'''”可以作为回调,且不会出现死循环; | ||
* 如果只想对特定的方法进行拦截,对其他的方法直接放行: | |||
*: “enhancer.setCallbackFilter(callbackHelper);” | |||
| | | | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java" line highlight="7-9,11,13,18"> | ||
public class SampleClass { | public class SampleClass { | ||
public void test(){ | public void test(){ | ||
| 第308行: | 第307行: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''ImmutableBean''' | |||
| 不可变的Bean | |||
* ImmutableBean允许创建一个原来对象的包装类,这个包装类是'''不可变的''',任何改变底层对象的包装类操作都会抛出'''IllegalStateException'''。 | |||
* 但是可以通过直接操作底层对象来改变包装类对象。 | |||
| | | | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
public class SampleBean { | |||
private String value; | |||
public SampleBean() { | |||
} | |||
public SampleBean(String value) { | |||
this.value = value; | |||
} | |||
public String getValue() { | |||
return value; | |||
} | |||
public void setValue(String value) { | |||
this.value = value; | |||
} | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
@Test(expected = IllegalStateException.class) | |||
public void testImmutableBean() throws Exception{ | |||
SampleBean bean = new SampleBean(); | |||
bean.setValue("Hello world"); | |||
SampleBean immutableBean = (SampleBean) ImmutableBean.create(bean); //创建不可变类 | |||
Assert.assertEquals("Hello world",immutableBean.getValue()); | |||
bean.setValue("Hello world, again"); //可以通过底层对象来进行修改 | |||
Assert.assertEquals("Hello world, again", immutableBean.getValue()); | |||
immutableBean.setValue("Hello cglib"); //直接修改将throw exception | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | '''Bean generator''' | ||
| | | cglib提供的一个操作bean的工具,使用它能够在运行时动态的创建一个bean。 | ||
| | | | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
@Test | |||
public void testBeanGenerator() throws Exception{ | |||
BeanGenerator beanGenerator = new BeanGenerator(); | |||
beanGenerator.addProperty("value",String.class); | |||
Object myBean = beanGenerator.create(); | |||
Method setter = myBean.getClass().getMethod("setValue",String.class); | |||
setter.invoke(myBean,"Hello cglib"); | |||
Method getter = myBean.getClass().getMethod("getValue"); | |||
Assert.assertEquals("Hello cglib",getter.invoke(myBean)); | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''Bean Copier''' | |||
| cglib提供的能够从一个bean复制到另一个bean中,而且其还提供了一个转换器,用来在转换的时候对bean的属性进行操作。 | |||
| | | | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | |||
public class OtherSampleBean { | |||
private String value; | |||
public String getValue() { | |||
return value; | |||
} | |||
public void setValue(String value) { | |||
this.value = value; | |||
} | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | |||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
@Test | |||
public void testBeanCopier() throws Exception{ | |||
BeanCopier copier = BeanCopier.create(SampleBean.class, OtherSampleBean.class, false);//设置为true,则使用converter | |||
SampleBean myBean = new SampleBean(); | |||
myBean.setValue("Hello cglib"); | |||
OtherSampleBean otherBean = new OtherSampleBean(); | |||
copier.copy(myBean, otherBean, null); //设置为true,则传入converter指明怎么进行转换 | |||
assertEquals("Hello cglib", otherBean.getValue()); | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | '''BulkBean''' | ||
| | | 复制bean,BulkBean将copy的动作拆分为getPropertyValues和setPropertyValues两个方法,允许自定义处理属性; | ||
* 避免每次进行BulkBean.create创建对象,一般将其声明为static的 | |||
* 应用场景:针对特定属性的get,set操作,一般适用通过xml配置注入和注出的属性,运行时才确定处理的Source,Target类,只需要关注属性名即可。 | |||
| | | | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
@Test | |||
public void testBulkBean() throws Exception{ | |||
BulkBean bulkBean = BulkBean.create(SampleBean.class, | |||
new String[]{"getValue"}, | |||
new String[]{"setValue"}, | |||
new Class[]{String.class}); | |||
SampleBean bean = new SampleBean(); | |||
bean.setValue("Hello world"); | |||
Object[] propertyValues = bulkBean.getPropertyValues(bean); | |||
assertEquals(1, bulkBean.getPropertyValues(bean).length); | |||
assertEquals("Hello world", bulkBean.getPropertyValues(bean)[0]); | |||
bulkBean.setPropertyValues(bean,new Object[]{"Hello cglib"}); | |||
assertEquals("Hello cglib", bean.getValue()); | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | '''BeanMap''' | ||
| | | BeanMap类实现了Java Map,将一个bean对象中的所有属性转换为一个String-to-Obejct的Java Map | ||
| | | | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
@Test | |||
public void testBeanMap() throws Exception{ | |||
BeanGenerator generator = new BeanGenerator(); | |||
generator.addProperty("username",String.class); | |||
generator.addProperty("password",String.class); | |||
Object bean = generator.create(); | |||
Metod setUserName = bean.getClass().getMethod("setUsername", String.class); | |||
Method setPassword = bean.getClass().getMethod("setPassword", String.class); | |||
setUserName.invoke(bean, "admin"); | |||
setPassword.invoke(bean,"password"); | |||
BeanMap map = BeanMap.create(bean); | |||
Assert.assertEquals("admin", map.get("username")); | |||
Assert.assertEquals("password", map.get("password")); | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | keyFactory | ||
| | | eyFactory类用来动态生成接口的实例,接口需要只包含一个newInstance方法,返回一个Object。keyFactory为构造出来的实例动态生成了Object.equals和Object.hashCode方法,能够确保相同的参数构造出的实例为单例的。 | ||
| | | | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
| 第412行: | 第495行: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | '''FastClass''' | ||
| | | 对Class对象进行特定的处理,比如通过数组保存method引用,因此FastClass引出了一个index下标的新概念,比如getIndex(String name, Class[] parameterTypes)就是以前的获取method的方法。 | ||
* 通过数组存储method,constructor等class信息,从而将原先的反射调用,转化为class.index的直接调用,从而体现所谓的FastClass。 | |||
| | | | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
@Test | |||
public void testFastClass() throws Exception{ | |||
FastClass fastClass = FastClass.create(SampleBean.class); | |||
FastMethod fastMethod = fastClass.getMethod("getValue",new Class[0]); | |||
SampleBean bean = new SampleBean(); | |||
bean.setValue("Hello world"); | |||
assertEquals("Hello world",fastMethod.invoke(bean, new Object[0])); | |||
} | |||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
|} | |} | ||
2020年10月29日 (四) 05:08的版本
关于代理
代理,简单说就是:不直接操作对象,而使用代理对象来完成操作;
- 通过代理对象,可以对原对象进行方法扩展;
代理又可以分为
- 静态代理:通过聚合、继承的方式生成代理对象;
- 代理关系在编译时就确定了
- 动态代理:
- 运行期动态生成代理对象;
- Java动态代理:(针对实现了接口的类)
- CGLIB:(针对没有实现接口的类)
- AspectJ:(springframework的aop基于此实现)
Java动态代理
invoke方法的自动调用
Java中动态代理的实现,关键在于:“Proxy”、“InvocationHandler”的关联;
以实例分析:
- 抽象接口:
//抽象角色(动态代理只能代理接口) public interface Subject { public void request(); }
- 抽象接口实现:
//真实角色:实现了Subject的request()方法 public class RealSubject implements Subject{ public void request(){ System.out.println("From real subject."); } }
- “InvocationHandler”接口的实现类:
//实现了InvocationHandler public class DynamicSubject implements InvocationHandler { private Object obj;//这是动态代理的好处,被封装的对象是Object类型,接受任意类型的对象 public DynamicSubject() { } public DynamicSubject(Object obj) { this.obj = obj; } //这个方法不是我们显示的去调用 public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.println("before calling " + method); method.invoke(obj, args); System.out.println("after calling " + method); return null; } }
- “invoke”方法进行代理处理逻辑,并调用对应的接口方法;
- 使用“method.invoke(obj, args);”,而不能使用“method.invoke(proxy, args); ”(后者将会导致死循环);
- “obj”:类型为“RealSubject”(由下面测试类中,初始化“DynamicSubject”的参数而来):
- “proxy”:就是代理实例“$Proxy0”:
- “method.invoke(proxy, args);”将会调用“$Proxy0”的method方法;
- 而“$Proxy0”的method方法,会执行“super.h.invoke(this, m3, null);”,即调用此处,从而调用陷入死循环;
- 测试类:
//客户端:生成代理实例,并调用了request()方法 public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable{ Subject rs = new RealSubject();//这里指定被代理类 InvocationHandler ds = new DynamicSubject(rs); Class<?> cls = rs.getClass(); //以下是一次性生成代理 Subject subject=(Subject) Proxy.newProxyInstance(cls.getClassLoader(),cls.getInterfaces(), ds); //这里可以看出subject的Class类是$Proxy0,这个$Proxy0类继承了Proxy,实现了Subject接口 System.out.println("subject的Class类是:"+subject.getClass().toString()); System.out.println("subject的父类是:"+subject.getClass().getSuperclass()); System.out.print("\n"+"subject实现的接口是:"); Class<?>[] interfaces=subject.getClass().getInterfaces(); for(Class<?> i:interfaces){ System.out.print(i.getName()+", "); } System.out.print("\n"+"subject中的属性有:"); Field[] field=subject.getClass().getDeclaredFields(); for(Field f:field){ System.out.print(f.getName()+", "); } System.out.print("\n"+"subject中的方法有:"); Method[] method=subject.getClass().getDeclaredMethods(); for(Method m:method){ System.out.print(m.getName()+", "); } System.out.println("\n\n"+"运行结果为:"); subject.request(); } }
- 运行结果如下:
subject的Class类是:class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0 subject的父类是:class java.lang.reflect.Proxy subject实现的接口是:Test1.Subject, subject中的属性有:m1, m2, m3, m0, subject中的方法有:equals, toString, hashCode, request, 运行结果为: before calling public abstract void Test1.Subject.request() From real subject. after calling public abstract void Test1.Subject.request()
- 如果初始化“DynamicSubject”时,传入参数不是“RealSubject”类型,则,DynamicSubject中的“method.invoke(obj, args); ”将不能执行:
- 错误信息:“object is not an instance of declaring class”
- “Proxy”的部分源码:
class Proxy{ InvocationHandler h=null; protected Proxy(InvocationHandler h) { this.h = h; } ... public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h) }
- Proxy 会生成一个“由loader加载”、“继承于Proxy”、“实现了interfaces等接口”的代理类“$Proxy0”;
- Proxy 会将“InvocationHandler”实例保存在属性中;
- 生成的“$Proxy0”:
public final class $Proxy0 extends Proxy implements Subject { private static Method m1; private static Method m0; private static Method m3; private static Method m2; static { try { m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("equals", new Class[] { Class.forName("java.lang.Object") }); m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("hashCode", new Class[0]); m3 = Class.forName("***.RealSubject").getMethod("request", new Class[0]); m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object").getMethod("toString", new Class[0]); } catch (NoSuchMethodException nosuchmethodexception) { throw new NoSuchMethodError(nosuchmethodexception.getMessage()); } catch (ClassNotFoundException classnotfoundexception) { throw new NoClassDefFoundError(classnotfoundexception.getMessage()); } } //static public $Proxy0(InvocationHandler invocationhandler) { super(invocationhandler); } @Override public final boolean equals(Object obj) { try { return ((Boolean) super.h.invoke(this, m1, new Object[] { obj })) .booleanValue(); } catch (Throwable throwable) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable); } } @Override public final int hashCode() { try { return ((Integer) super.h.invoke(this, m0, null)).intValue(); } catch (Throwable throwable) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable); } } public final void request() { try { super.h.invoke(this, m3, null); return; } catch (Error e) { } catch (Throwable throwable) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable); } } @Override public final String toString() { try { return (String) super.h.invoke(this, m2, null); } catch (Throwable throwable) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(throwable); } } }
- 其中“m1”、“m0”、“m3”、“m2”是“Method”类型的字段,表示“$Proxy0”中方法所对应的原方法;包括:
- 继承于“Object”的“equals”(m1)、“hashCode”(m0)、“toString”(m2)
- 实现“Subject”的“request”(m3);
- “$Proxy0”的方法实现:“super.h.invoke(this, m3, null);”:
- 调用父类的“h”(“InvocationHandler”实例)的“invoke”方法;(“invoke”中进行代理处置,并调用原始方法)
- 参数:“this”($Proxy0)、“m2”(原始方法)、“null”(方法参数)
AspectJ
- 参见:Spring:AOP
CGLIB
CGLIB是一个功能强大,高性能的代码生成包。
- 使用CGLib实现动态代理,完全不受代理类必须实现接口的限制;
- CGLib底层采用ASM字节码生成框架,使用字节码技术生成代理类,比使用Java反射效率要高。
原理
- 动态生成一个要代理类的子类,子类重写要代理的类的所有不是final的方法。
- 在子类中采用方法拦截的技术,拦截所有父类方法的调用,并织入横切逻辑。
- 为没有实现接口的类提供代理,比于JDK动态代理(只能代理接口)更加强大;
- 不能代理final方法;
CGLIB组成结构
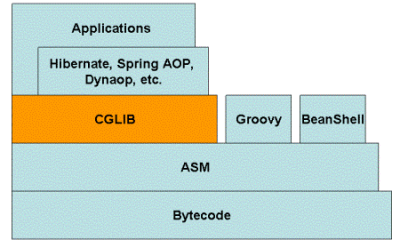
CGLIB底层使用了ASM(一个短小精悍的字节码操作框架)来操作字节码生成新的类。
- 因为使用字节码技术生成代理类,所以CGLIB比java反射的JDK动态代理更快;
- 关于“ASM”:
- 除了CGLIB库外,脚本语言(如:“Groovy”、“BeanShell”)也使用ASM生成字节码;
- ASM使用类似SAX的解析器来实现高性能;
- (如果直接使用ASM,需要对Java字节码非常了解)
jar包
- “cglib-nodep-2.2.jar”:使用nodep包不需要关联asm的jar包,jar包内部包含asm的类.
- “cglib-2.2.jar”:使用此jar包需要关联asm的jar包,否则运行时报错.
类库
CGLIB类库:
- “net.sf.cglib.core”:底层字节码处理类,他们大部分与ASM有关系;
- “net.sf.cglib.transform”:编译期或运行期类和类文件的转换;
- “net.sf.cglib.proxy”:实现创建代理和方法拦截器的类;
- “net.sf.cglib.reflect”:实现快速反射和C#风格代理的类;
- “net.sf.cglib.util”:集合排序等工具类;
- “net.sf.cglib.beans”:JavaBean相关的工具类;
常用的API
| 命令 | 说明 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| Enhancer | Enhancer创建一个被代理对象的子类并且拦截所有的方法调用(包括从Object中继承的toString和hashCode方法)
|
public class SampleClass {
public void test(){
System.out.println("hello world");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(SampleClass.class);
enhancer.setCallback(new MethodInterceptor() {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("before method run...");
Object result = proxy.invokeSuper(obj, args);
System.out.println("after method run...");
return result;
}
});
SampleClass sample = (SampleClass) enhancer.create();
sample.test();
}
}
输出: before method run...
hello world
after method run...
|
| ImmutableBean | 不可变的Bean
|
public class SampleBean {
private String value;
public SampleBean() {
}
public SampleBean(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
@Test(expected = IllegalStateException.class)
public void testImmutableBean() throws Exception{
SampleBean bean = new SampleBean();
bean.setValue("Hello world");
SampleBean immutableBean = (SampleBean) ImmutableBean.create(bean); //创建不可变类
Assert.assertEquals("Hello world",immutableBean.getValue());
bean.setValue("Hello world, again"); //可以通过底层对象来进行修改
Assert.assertEquals("Hello world, again", immutableBean.getValue());
immutableBean.setValue("Hello cglib"); //直接修改将throw exception
}
|
| Bean generator | cglib提供的一个操作bean的工具,使用它能够在运行时动态的创建一个bean。 |
@Test
public void testBeanGenerator() throws Exception{
BeanGenerator beanGenerator = new BeanGenerator();
beanGenerator.addProperty("value",String.class);
Object myBean = beanGenerator.create();
Method setter = myBean.getClass().getMethod("setValue",String.class);
setter.invoke(myBean,"Hello cglib");
Method getter = myBean.getClass().getMethod("getValue");
Assert.assertEquals("Hello cglib",getter.invoke(myBean));
}
|
| Bean Copier | cglib提供的能够从一个bean复制到另一个bean中,而且其还提供了一个转换器,用来在转换的时候对bean的属性进行操作。 |
public class OtherSampleBean {
private String value;
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
@Test
public void testBeanCopier() throws Exception{
BeanCopier copier = BeanCopier.create(SampleBean.class, OtherSampleBean.class, false);//设置为true,则使用converter
SampleBean myBean = new SampleBean();
myBean.setValue("Hello cglib");
OtherSampleBean otherBean = new OtherSampleBean();
copier.copy(myBean, otherBean, null); //设置为true,则传入converter指明怎么进行转换
assertEquals("Hello cglib", otherBean.getValue());
}
|
| BulkBean | 复制bean,BulkBean将copy的动作拆分为getPropertyValues和setPropertyValues两个方法,允许自定义处理属性;
|
@Test
public void testBulkBean() throws Exception{
BulkBean bulkBean = BulkBean.create(SampleBean.class,
new String[]{"getValue"},
new String[]{"setValue"},
new Class[]{String.class});
SampleBean bean = new SampleBean();
bean.setValue("Hello world");
Object[] propertyValues = bulkBean.getPropertyValues(bean);
assertEquals(1, bulkBean.getPropertyValues(bean).length);
assertEquals("Hello world", bulkBean.getPropertyValues(bean)[0]);
bulkBean.setPropertyValues(bean,new Object[]{"Hello cglib"});
assertEquals("Hello cglib", bean.getValue());
}
|
| BeanMap | BeanMap类实现了Java Map,将一个bean对象中的所有属性转换为一个String-to-Obejct的Java Map |
@Test
public void testBeanMap() throws Exception{
BeanGenerator generator = new BeanGenerator();
generator.addProperty("username",String.class);
generator.addProperty("password",String.class);
Object bean = generator.create();
Metod setUserName = bean.getClass().getMethod("setUsername", String.class);
Method setPassword = bean.getClass().getMethod("setPassword", String.class);
setUserName.invoke(bean, "admin");
setPassword.invoke(bean,"password");
BeanMap map = BeanMap.create(bean);
Assert.assertEquals("admin", map.get("username"));
Assert.assertEquals("password", map.get("password"));
}
|
| keyFactory | eyFactory类用来动态生成接口的实例,接口需要只包含一个newInstance方法,返回一个Object。keyFactory为构造出来的实例动态生成了Object.equals和Object.hashCode方法,能够确保相同的参数构造出的实例为单例的。 | |
| FastClass | 对Class对象进行特定的处理,比如通过数组保存method引用,因此FastClass引出了一个index下标的新概念,比如getIndex(String name, Class[] parameterTypes)就是以前的获取method的方法。
|
@Test
public void testFastClass() throws Exception{
FastClass fastClass = FastClass.create(SampleBean.class);
FastMethod fastMethod = fastClass.getMethod("getValue",new Class[0]);
SampleBean bean = new SampleBean();
bean.setValue("Hello world");
assertEquals("Hello world",fastMethod.invoke(bean, new Object[0]));
}
|
使用
-
public class TargetObject { public String method1(String paramName) { return paramName; } public int method2(int count) { return count; } public int method3(int count) { return count; } @Override public String toString() { return "TargetObject []"+ getClass(); } }